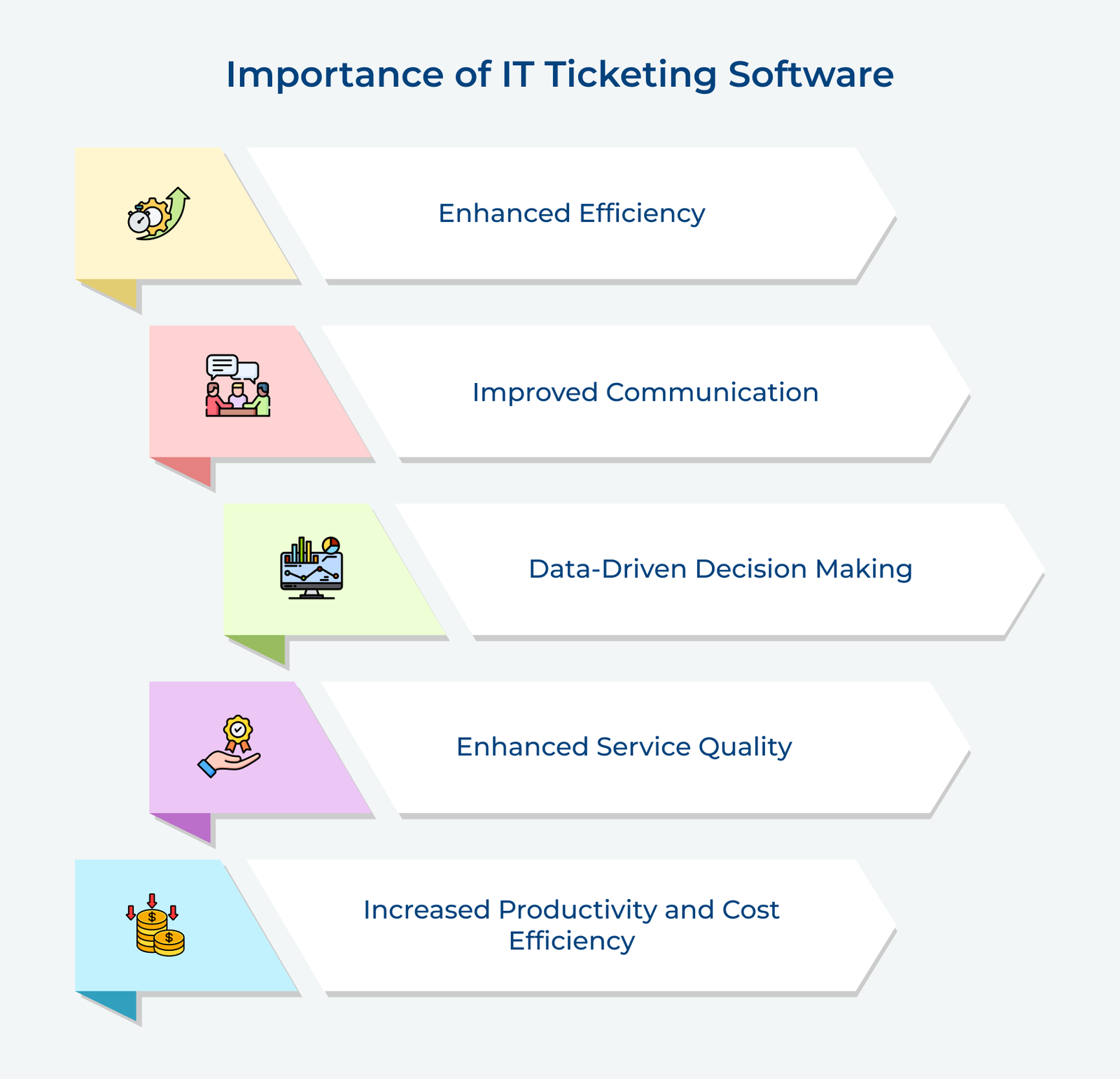
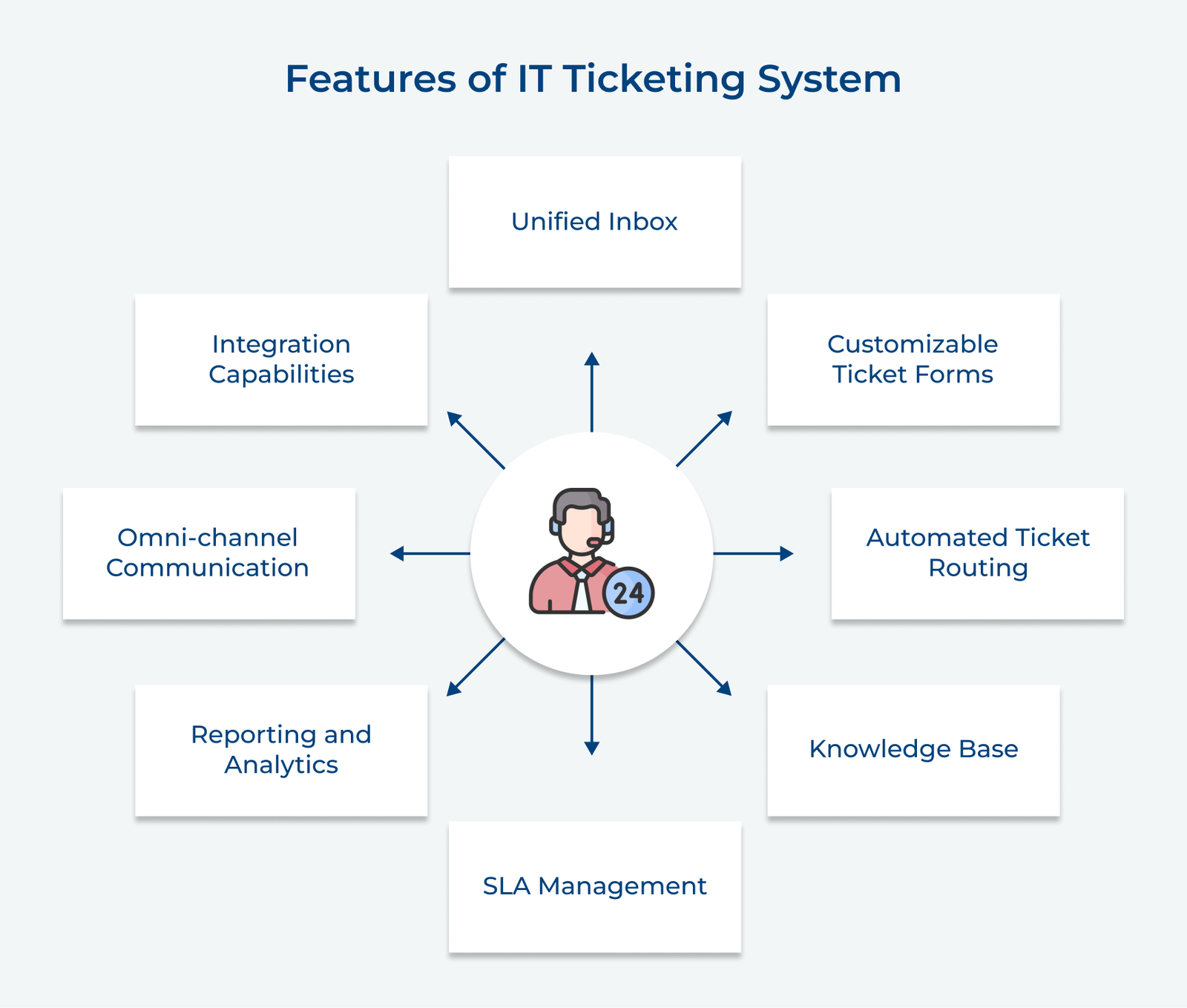
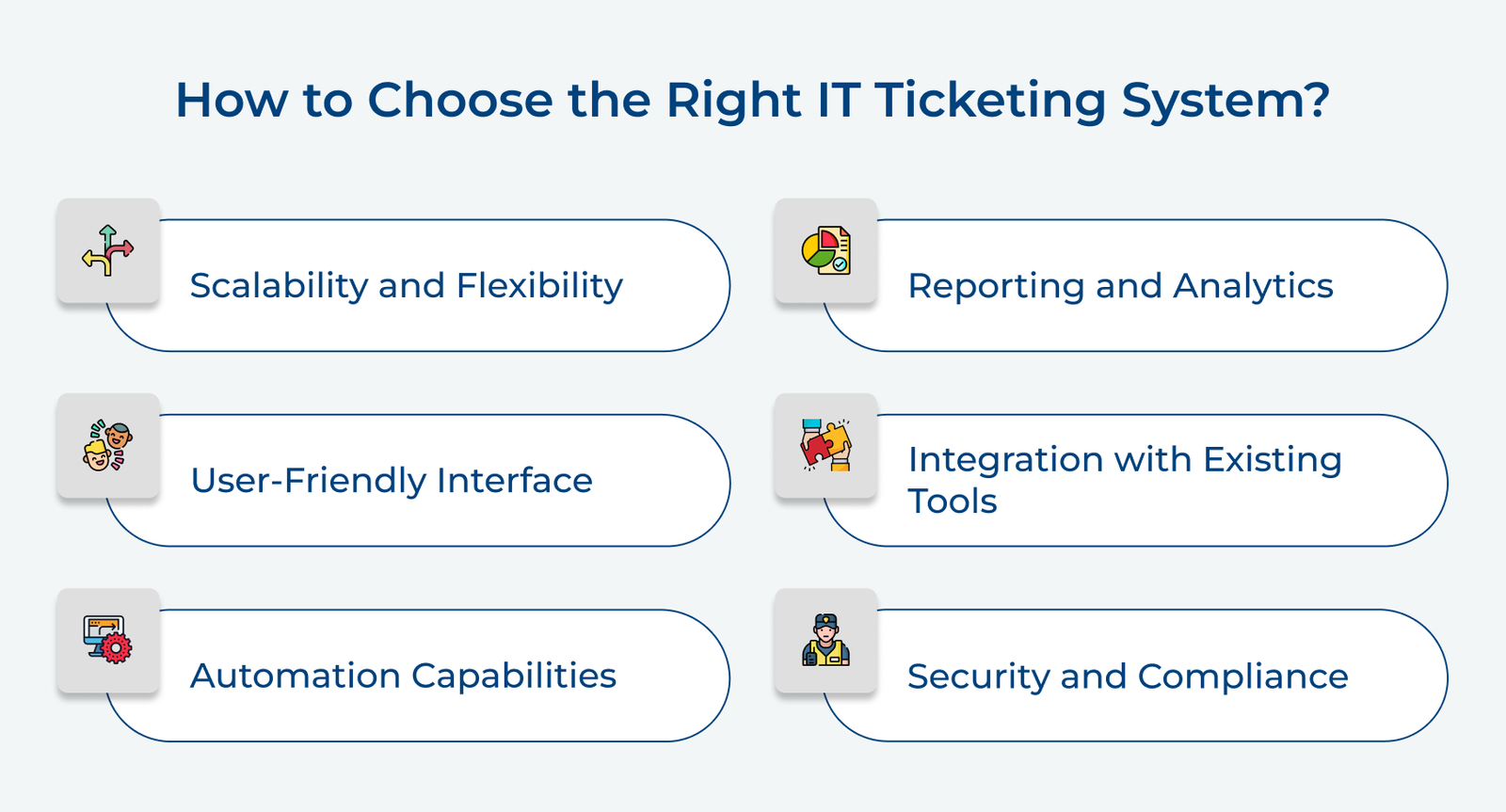
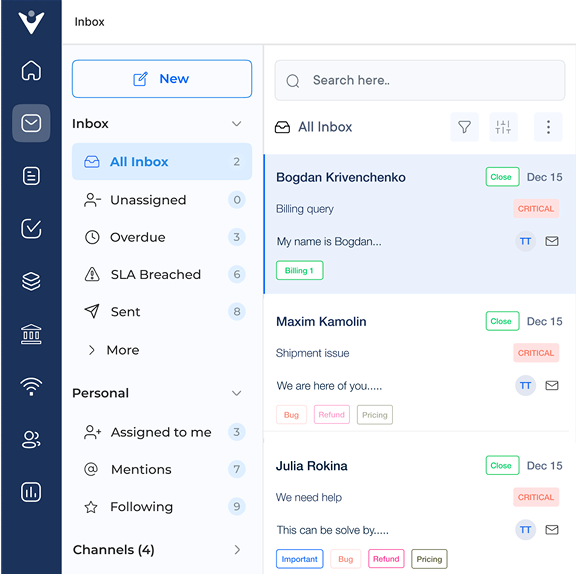
1. Implement a Clear Categorization System
Implementing a clear categorization system is crucial for effective IT ticketing solutions.
Use standardized categories to organize tickets consistently, such as “Hardware,” “Software” and “Network,” with subcategories like “Printer Issues” or “Email Problems.”
The structure ensures easy navigation and quick issue identification, allowing support staff to efficiently locate tickets.
Pro tips:
- Regularly update categories to reflect evolving technology and common issues, keeping the system relevant.
- Implement a search function with keyword recognition to help users find the right category quickly, reducing misfiled tickets and improving response times.
- Provide clear guidelines for both end-users and support staff on how to use the categorization system effectively.
2. Establish Priority Levels and SLAs
Establishing priority levels and Service Level Agreements (SLAs) is crucial for effective IT ticketing solutions. Define clear priority levels such as low, medium, high and critical to categorize incoming tickets based on urgency.
Set and communicate specific SLAs for each priority level. The agreements should outline the expected response and resolution times as shown in the example below:
- Critical: 15-minute response, 2-hour resolution
- High: 1-hour response, 8-hour resolution
- Medium: 4-hour response, 24-hour resolution
- Low: 8-hour response, 72-hour resolution
Pro tips:
- Regularly adjust priority levels and SLAs based on team capacity.
- Implement an escalation process for tickets that risk breaching SLAs.
- Use automation to assign priority levels based on predefined criteria, ensuring consistency and reducing manual effort.
3. Automate Ticket Routing and Assignment
Automating ticket routing and assignment is a key best practice for an efficient IT ticketing solution. Use rules-based routing to direct tickets to appropriate teams or individuals based on factors like issue type, urgency, or required expertise.
Let’s consider that a large e-commerce company implements automated routing for its customer support tickets. When a customer reports a payment issue, the system automatically assigns it to the finance team. If it’s a shipping query, it’s routed to logistics. High-priority tickets are distributed among available senior staff to ensure quick resolution.
Pro tips:
- Regularly review and update routing rules to adapt to changing team structures or new types of issues.
- Incorporate skills-based routing to match complex tickets with the most qualified staff.
- Use AI-powered routing to learn from past ticket resolutions and improve assignment accuracy over time.
4. Maintain Detailed and Standardized Documentation
Maintaining detailed and standardized documentation is a critical best practice for IT ticketing solutions. Create templates for common issues to ensure consistent information gathering and streamline the resolution process. The templates should include fields for essential details like problem description, affected systems and troubleshooting steps.
Let’s assume that a company implements standardized documentation for its IT helpdesk. When a user reports a recurring network connectivity issue, the support team quickly accesses a relevant template and resolves the problem efficiently.
Pro tips:
- Implement a searchable knowledge base to make documentation easily accessible.
- Regularly review and update the documentation to ensure accuracy.
- Use clear, concise language and include visuals when appropriate to enhance understanding.
5. Utilize a Knowledge Base
Utilizing a knowledge base is vital for implementing an IT ticketing solution. Develop and maintain a searchable repository of common issues, solutions and procedures. The resource empowers both support staff and end-users to find answers quickly, reducing ticket volume.
Let’s assume that an employee submits a ticket about email synchronization issues. The ticketing system automatically suggests knowledge-based articles about common email problems. The support agent will quickly find a relevant solution and resolve the issue. It will simultaneously update the ticket and reference the knowledge base article used.
Pro tips:
- Encourage agents to contribute to the knowledge base, creating articles from recurring issues they solve.
- Implement a regular review process to keep content up-to-date and relevant.
- Use analytics to identify frequently accessed articles and optimize them for better user experience.
6. Implement Regular Reporting and Analytics
Implementing regular reporting and analytics is essential for optimizing IT ticketing solutions. Track key performance indicators (KPIs) such as average response time, resolution time, first-contact resolution rate and customer satisfaction scores.
Let’s assume that a company noticed a spike in password reset tickets every Monday morning. They implemented a self-service password reset tool by analyzing the trend. The approach helped in reducing the ticket volume of the business.
Pro tips:
- Create customizable dashboards for different stakeholders, allowing quick access to relevant metrics.
- Set up automated reports to be sent regularly, ensuring consistent monitoring and analysis.
- Use predictive analytics to forecast future ticket volumes and plan resources.
7. Promote Communication and Collaboration
Promoting communication and collaboration is essential when implementing an IT ticketing solution. Enable easy updates within tickets by integrating comment threads, status updates and notification systems. All the stakeholders will remain informed throughout the ticket’s lifecycle.
Let’s imagine that a critical server outage takes place. The ticketing system will allow multiple technicians to collaborate simultaneously, sharing diagnostics and progress updates in real time. The coordinated effort will eventually result in faster resolution and minimize downtime.
Pro tips:
- Integrate the ticketing system with communication tools like Slack or Microsoft Teams for seamless information flow.
- Implement a mentorship program where senior technicians can guide junior staff through complex tickets, enhancing knowledge transfer.
- Regularly conduct post-mortem meetings for major incidents, using the ticketing system’s data to analyze response effectiveness.