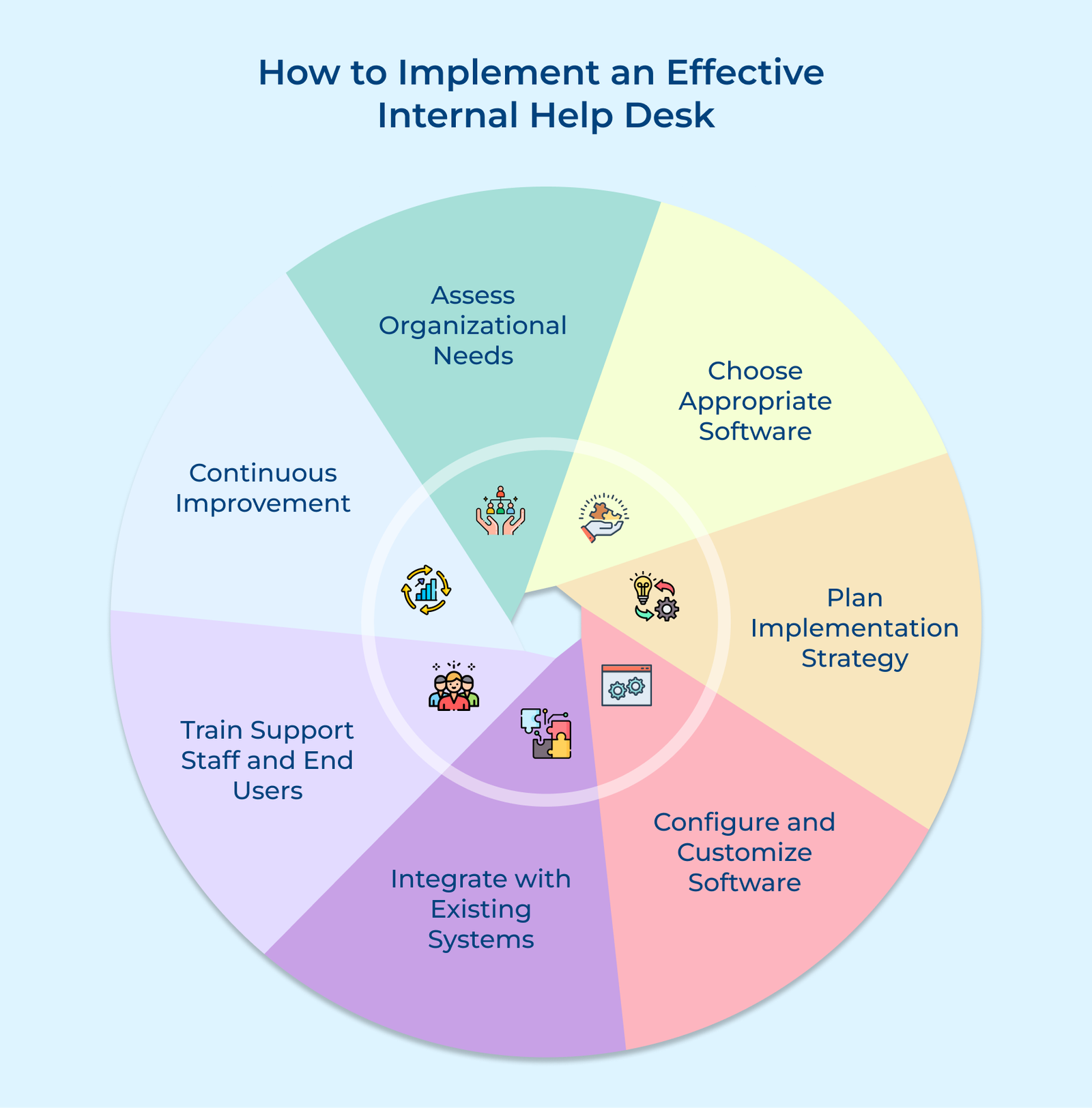
1. Assess Organizational Needs
Assessing organizational needs is crucial for implementing an effective internal help desk. Identify common support issues by analyzing user complaints, tracking recurring problems and surveying employees. The comprehensive data helps the teams prioritize areas requiring immediate attention.
Evaluate current processes by reviewing existing support mechanisms, gathering feedback from both support staff and end-users. The assessment makes the business understand which areas need improvement or changes.
Pro tips:
- Involve stakeholders from various departments to gain diverse perspectives on support requirements.
- Use data analytics tools to uncover patterns in support requests, helping predict future needs and trends.
- Conduct regular reassessments to ensure the help desk evolves with changing organizational needs and technological advancements.
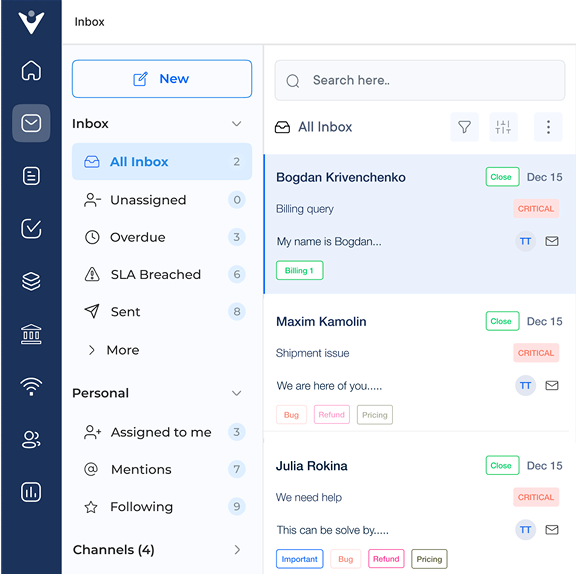
2. Choose Appropriate Software
Research available solutions by evaluating options to ensure you choose the right fit for your business needs. Consider factors such as scalability, integration capabilities and user-friendliness. Make sure to read reviews, compare features and request demos to gain hands-on experience.
Select software that aligns with organizational needs by assessing the company’s size, budget and specific requirements. Consider factors like ticket management, knowledge base functionality and reporting capabilities. Ensure the chosen solution can grow with the organization and integrate with existing systems.
Best practices:
- Prioritize user adoption by selecting an intuitive interface that requires minimal training for both agents and end-users.
- Consider cloud-based solutions for easier implementation, maintenance and accessibility from multiple locations.
- Look for customization options to tailor the software to the organization’s unique workflows and branding.
3. Plan Implementation Strategy
Set clear objectives and timelines for the help desk implementation, ensuring the strategy is aligned with the goals of the business. Define specific, measurable targets and establish realistic deadlines for each phase of the project. Assign roles and responsibilities to team members, clearly outlining their duties.
Develop a comprehensive change management plan to address potential resistance and facilitate smooth adoption. It should include communication strategies, training programs and feedback mechanisms.
Ways to implement:
- Prioritize user experience by involving end-users in the design and testing phases, ensuring the help desk meets their needs effectively.
- Establish continuous improvement processes, regularly updating help desk procedures based on user feedback and emerging best practices.
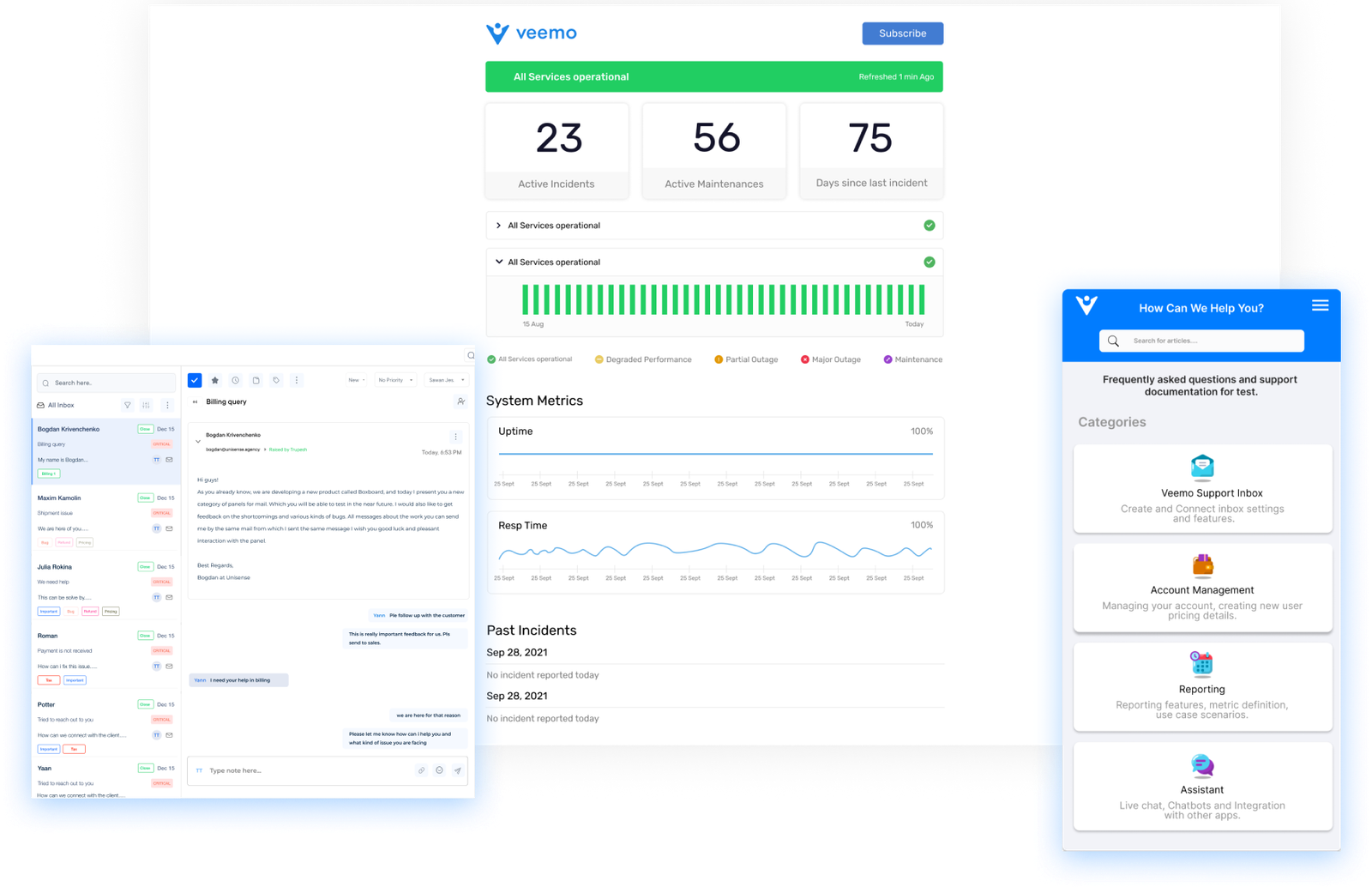
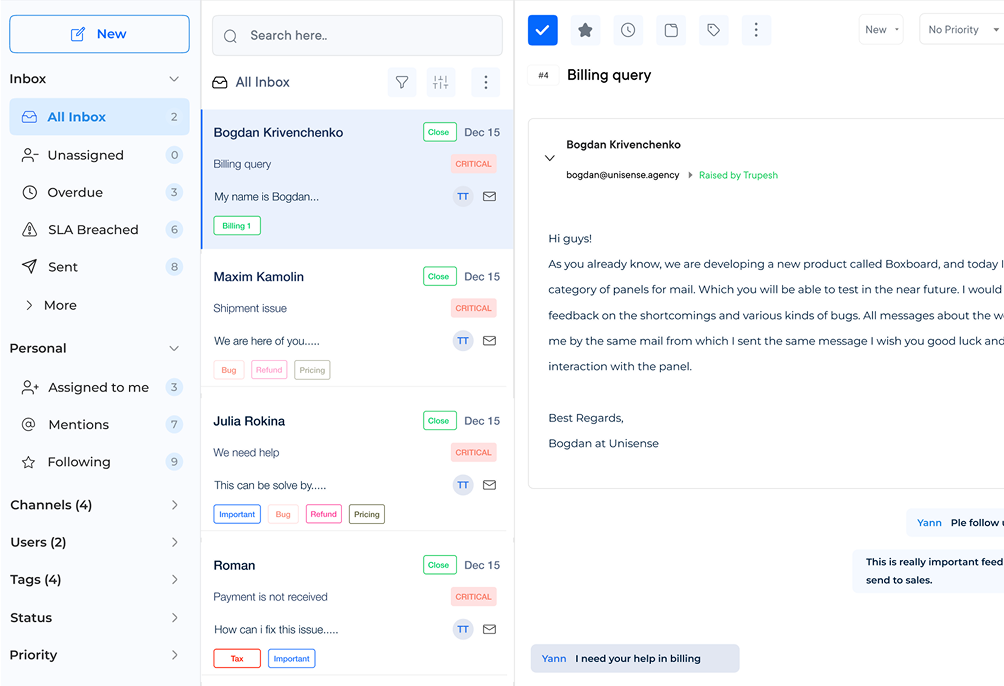
4. Configure and Customize Software
Start by setting up a robust ticketing system with customized workflows. Define ticket categories, priorities and escalation paths to streamline issue resolution. Create automated routing rules to assign tickets to appropriate teams based on predefined criteria.
Customize the user interface to align with the organization’s branding and improve user experience. Modify color schemes, logos and layouts to create a familiar environment for employees. Make sure the interface is intuitive and responsive across devices.
Best practices:
- Integrate the help desk software with other internal tools for seamless data flow and improved efficiency.
- Implement single sign-on (SSO) for easy access and enhanced security.
- Regularly analyze usage data and user feedback to continually refine the system.
5. Integrate with Existing Systems
Integrating an internal help desk with existing systems is crucial for its efficiency and effectiveness. Start by connecting with communication tools like Slack or Microsoft Teams, allowing seamless ticket creation and updates.
Integrating with asset management systems is also important to ensure the technicians have access to hardware and software information. Make sure there’s data synchronization across all platforms to maintain accuracy and prevent discrepancies.
Ways to implement:
- Implement single sign-on (SSO) for easy access and enhanced security across integrated systems.
- Use API integrations to automate workflows and reduce manual data entry, improving productivity.
- Regularly audit to maintain optimal performance and address any compatibility issues as systems evolve.
6. Train Support Staff and End Users
Training support staff and end users is crucial for implementing an effective internal help desk. Begin by conducting thorough training sessions for the IT team, covering technical skills, customer service and problem-solving techniques.
Create comprehensive user guides for employees, explaining common issues and step-by-step solutions. Offer ongoing support, including regular refresher courses and updates on new systems or procedures. Both support staff and end users can stay current with evolving technologies.
Pro tips:
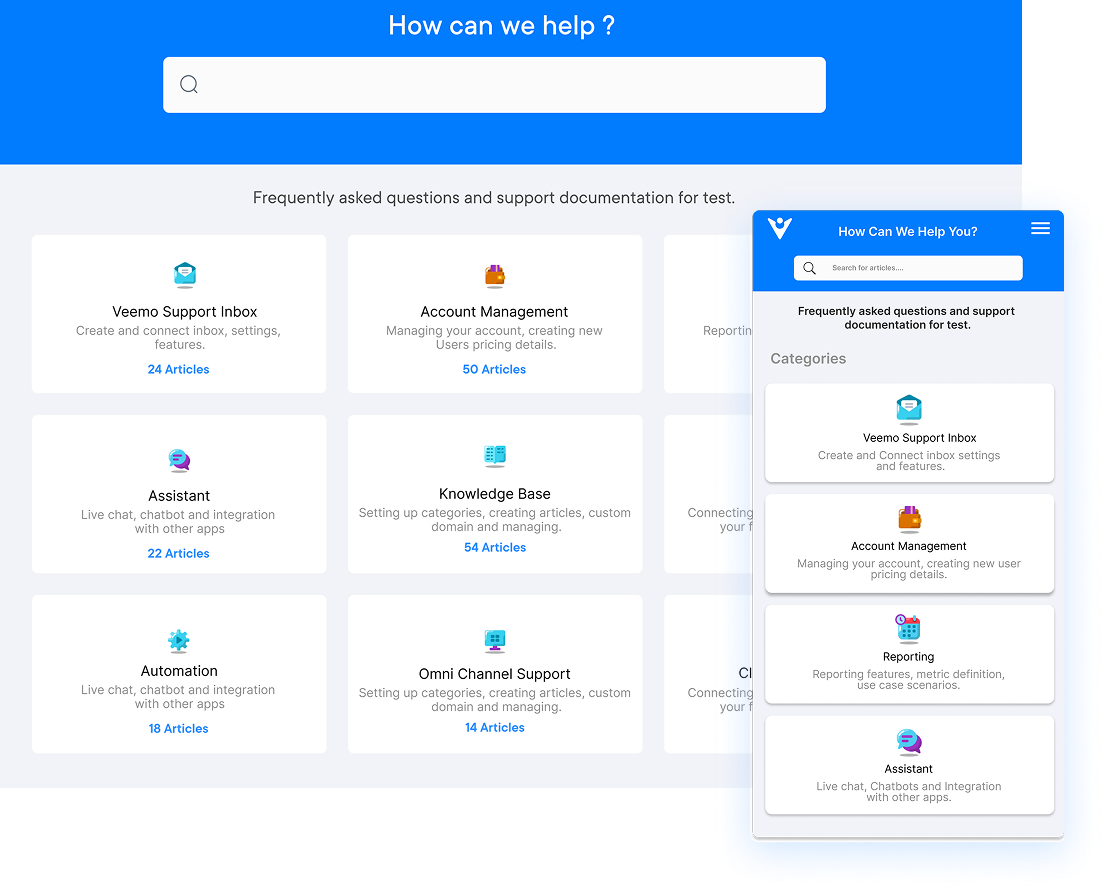
- Utilize a knowledge base or FAQ section to empower support staff to find solutions and provide them to the end user quickly.
- Regularly collect feedback from end users to continually improve the performance of the support staff with effective training.
7. Continuous Improvement
Continuous improvement is crucial for implementing an effective internal help desk. Organizations can identify areas for enhancement and track progress over time by regularly analyzing performance data. The data-driven approach allows for informed decision-making and targeted improvements.
Soliciting user feedback is equally important as it provides valuable insights into the end-user experience and highlights potential pain points. The feedback can guide improvements in service delivery and user satisfaction. Updating processes and knowledge bases as needed ensures that the help desk remains current and efficient.
Key benefits:
- Increased efficiency: Streamlined processes lead to faster issue resolution and improved productivity.
- Enhanced user satisfaction: User satisfaction increases by addressing pain points and improving service quality.
- Adaptability: Regular improvements allow the help desk to evolve with changing organizational needs and technological advancements.