1. Tailored Experience
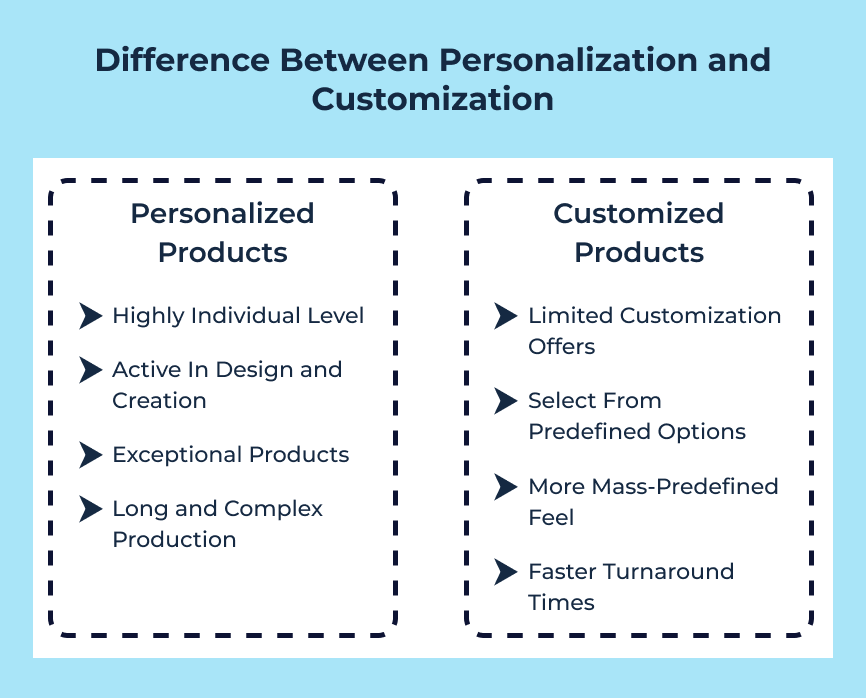
Personalization can provide a more seamless experience for customers by anticipating their needs and preferences. Analyzing customer behaviors allows businesses to tailor their offerings to each individual. It creates a more personalized and engaging experience.
Customization gives customers more control over their experience. It allows them to choose exactly what they want and how they want it. It can lead to higher customer satisfaction as customers feel empowered and valued by the ability to create their own unique experience.
Key takeaways:
- Personalization may be more effective for businesses with a large customer base and complex products or services.
- Customization may be more suitable for businesses looking to empower customers and create a sense of ownership over their experience.
2. Data Usage
Personalization relies on collecting and analyzing data about individual customer preferences to deliver tailored content. It requires businesses to utilize data on a granular level such as browsing history, purchase patterns and demographic information. Leveraging this data allows businesses to create a personalized experience that resonates with each customer on a personal level.
Customization involves offering a range of options for customers to choose from. It allows them to select features or products that best suit their preferences. The approach still requires data on customer preferences, but on a broader scale rather than on an individual level.
Key takeaways:
- Personalization is more intensive and requires a higher level of data collection. It can result in a more tailored and engaging experience for customers.
- Customization can be a more practical choice for businesses that may not have the resources for extensive data collection but still want to offer a customized touch to their customers.
3. Automation
Personalization focuses on tailoring content, products or services based on individual preferences or behavior. Personalization typically requires more advanced technology to analyze data and deliver personalized recommendations or messages in real-time.
Customization often involves more manual input from the customer such as selecting product features or design options. Customization involves giving customers the ability to choose and modify elements to suit their preferences.
Key takeaways:
- Personalization through automation can help businesses streamline processes and deliver targeted messages efficiently. It leads to more personalized interactions with customers.
- Customization through automation can empower customers to create their own unique experiences. Businesses must ensure a seamless and user-friendly interface to facilitate this process effectively.
4. Flexibility
Personalization is more limited as it relies on existing data and algorithms to make recommendations or adjustments. Customers may feel constrained by the options presented to them and may not have as much control over the outcome.
Customization provides a higher level of flexibility as customers can actively choose and adjust various features according to their preferences.
Key takeaways:
- A business looking to provide a more flexible customer experience, customization may be the better choice. Allowing customers to have more control over the products or services they receive enables businesses to cater to a wider range of preferences.
- Personalization can still be valuable for businesses seeking to streamline and optimize the customer journey. Using data-driven insights to personalize recommendations allows businesses to enhance the overall customer experience and drive loyalty.
5. Complexity
Personalization is highly effective in creating a personalized experience for customers. It can be more complex to implement due to the need for sophisticated data analysis and technology integration. It requires businesses to collect and analyze large amounts of customer data to deliver targeted content or recommendations.
Customization is more straightforward in terms of complexity as it involves providing customers with predetermined options to choose from. It may not offer the same level of individualization as personalization but customization still allows customers to have a say in their experience.
Key takeaways:
- Personalization may be the preferred option for businesses with advanced data analytics capabilities and technology infrastructure. It involves many complex processes.
- Customization may be a more feasible choice for smaller businesses with limited resources and hence less complex compared to personalization.
Examples of Personalization and Customization
Below are the real-life examples that illustrate how businesses are creatively meeting individual needs and reshaping the consumer experience.
A. Example of Personalization
1. Netflix
Netflix is a perfect example of a brand that excels at personalization. Netflix can provide users with personalized movie and TV show suggestions based on their viewing history through its recommendation algorithm. The level of personalization not only enhances the user experience but also keeps customers engaged and coming back for more. Netflix sends personalized emails with recommendations, reminders and updates, further solidifying their commitment to personalization.
2. Amazon
Amazon is another brand that has mastered the art of personalization. Analyzing customer data and purchase history allows Amazon to provide personalized product recommendations, offers and promotions to each customer. The level of personalization not only drives sales but also enhances the overall shopping experience for customers. Amazon uses personalized emails, on-site recommendations and targeted advertising to ensure that customers feel valued.
3. Spotify
Spotify is a music streaming service that has leveraged personalization to create a unique and engaging user experience. Spotify can cater to each user’s music preferences through their personalized playlists, recommendations and music discovery features. Curating personalized content, Spotify not only keeps users engaged but also encourages them to explore and discover new music. Spotify uses personalized emails, notifications and targeted ads to connect with users on a more personal level.
B. Customization Example
1. Nike
Nike is a prime example of a brand that focuses on customization through its Nike By You platform. Customers can personalize their shoes by choosing colors, materials and even adding custom text or graphics. It not only allows customers to create a one-of-a-kind product, but it also promotes a sense of ownership and self-expression. Nike By You has been a huge success, with customers willing to pay a premium for a custom-designed pair of shoes.
2. Coca-Cola
Coca-Cola is another brand that has embraced customization with its “Share a Coke” campaign. The campaign replaced the Coca-Cola logo with popular names, encouraging consumers to find a bottle with their name on it or purchase a personalized bottle for a friend. This simple idea has resonated with consumers and helped Coca-Cola strengthen its emotional connection with them. The campaign has been so successful that it has been replicated in various countries around the world.
3. McDonald’s
McDonald’s has also dabbled in customization with its “Create Your Taste” platform. It allows customers to build their burgers by choosing from a variety of ingredients and toppings. Customers can personalize everything from the type of bun to the sauce used, creating a burger that suits their specific tastes. The customization trend has been a hit with customers, who appreciate the ability to tailor their meals to their liking.
3 Use Cases of Personalization
Check out the compelling use cases of personalization that demonstrate how it plays a significant role across various industries.