Buyer Journey vs Customer Journey: 6 Key Differences
The buyer journey leads to a purchase. The customer journey focuses on the entire relationship. Understanding the buyer journey vs customer journey helps turn one-time buyers into brand advocates.

The buyer journey leads to a purchase. The customer journey focuses on the entire relationship. Understanding the buyer journey vs customer journey helps turn one-time buyers into brand advocates.

Have you ever wondered about the difference between a buyer journey and a customer journey? While they may sound similar, there are key distinctions between the two.
Understanding the various stages that a potential customer goes through before and after making a purchase is crucial for businesses looking to attract customers. The buyer journey and customer journey are both important concepts. It can help businesses tailor their marketing efforts to better meet the needs and expectations of their target audience.
We will delve into the differences between a buyer journey vs customer journey and explore how businesses can leverage the knowledge to create a more effective marketing strategy. So, if you’re looking to optimize your marketing efforts, keep reading.
The buyer journey refers to the process that a potential customer goes through before making a purchase. It includes the awareness stage, consideration stage and decision stage. During the awareness stage, the customer becomes aware of a need or problem. The customer evaluates different solutions to address their needs in the consideration stage. The customer makes a purchase decision in the decision stage.
Key objectives:
The buyer’s journey is a significant concept so understanding and implementing a buyer’s journey strategy can have numerous benefits for a business:
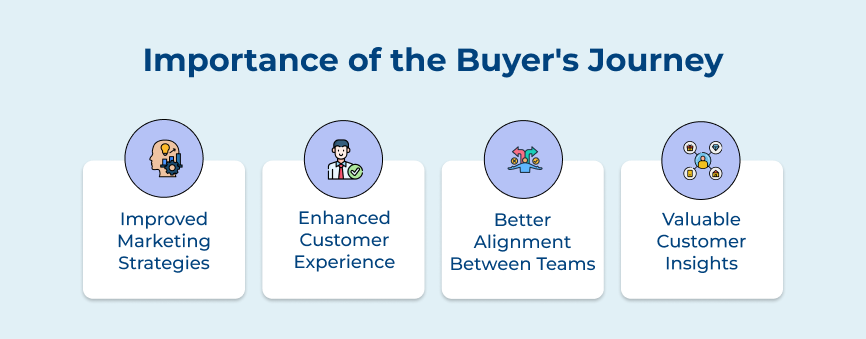
Mapping out the buyer’s journey can help businesses tailor their marketing strategies to target potential customers at each stage of the process. The approach allows companies to create personalized and targeted content that resonates with their audience. It leads to higher conversion rates and increased sales.
Understanding the needs and motivations of customers at each stage of the buyer’s journey can help businesses provide a more personalized buying experience. It can help build trust with customers, leading to repeat business and positive word-of-mouth referrals.
Implementing a buyer’s journey approach requires close collaboration between sales and marketing teams. Teams can create more cohesive strategies for engaging with customers and driving sales by working together to understand the buyer’s journey. The alignment can lead to higher efficiency and productivity within the organization.
Analyzing the buyer’s journey can provide businesses with valuable insights into their target audience’s preferences, behavior’s and pain points. Understanding how customers move through the purchasing process can help companies adjust their strategies. It helps them to better meet the needs of their customers and stay ahead of the competition.
The customer journey refers to the entire relationship that a customer has with a brand, from the moment they first hear about the brand to post-purchase interactions. It includes the pre-purchase, purchase and post-purchase stages. The pre-purchase stage involves building awareness and consideration, while the purchase stage includes the actual transaction. The post-purchase stage focuses on retaining and engaging customers to encourage repeat purchases.
key objectives:
Businesses cannot afford to neglect their customer’s journey, especially as it stretches from the customer’s initial contact till they become loyal customer. Here are five key benefits of focusing on the customer journey for your business:

Businesses can better understand their customer’s needs, preferences and pain points by mapping out the customer journey. It allows businesses to tailor their marketing and messaging to better engage with customers at each stage of their journey. The personalized approach can help businesses build stronger relationships with their customers and increase customer retention.
Understanding the customer journey can help businesses identify areas where customers may be dropping off or experiencing friction in the buying process. The insight can help businesses make improvements to their sales funnel and increase conversion rates. Businesses can see a significant increase in sales by removing barriers to purchase and making it easier for customers to buy.
Focusing on the customer journey can help businesses build stronger relationships with their customers and create more loyal customers. Providing a seamless experience can help businesses enhance trust and loyalty with customers. It leads to repeat purchases and positive word-of-mouth referrals.
Businesses that prioritize the customer journey are better positioned to stand out from the competition. Businesses can differentiate themselves in the market and attract customers by delivering a superior customer experience. It can lead to long-term success and growth for the business.
Leaders can better align their strategies to ensure a seamless transition from prospect to customer by understanding the similarities listed below:
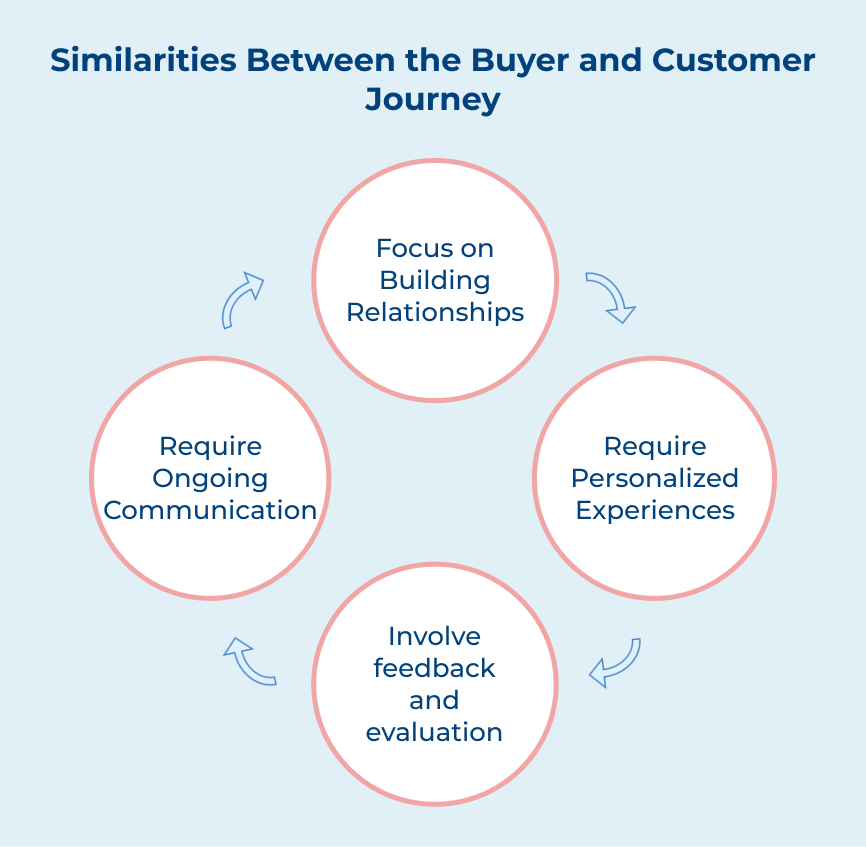
1. Both journeys focus on building relationships: The buyer’s journey and the customer’s journey are both focused on building relationships with individuals. During the buyer’s journey, marketers aim to create awareness, educate and engage potential customers. Once a purchase is made, the focus shifts to providing excellent customer service and personalized experiences. It helps to retain customers and encourage repeat purchases.
2. Both journeys require personalized experiences: Personalization is key in both the buyer’s journey and the customer’s journey. Marketers need to understand the needs, preferences and behavior of individuals at each stage of the journey to deliver relevant content. Personalizing experiences can help marketers increase engagement, conversions and loyalty.
3. Both journeys involve feedback and evaluation: Feedback and evaluation are both essential components. During the buyer’s journey, individuals may provide feedback on solution or messaging that can help marketers improve their strategies. After a purchase is made, customers may continue to provide feedback on their experience. It can be used to enhance the customer journey and improve satisfaction.
4. Both journeys require ongoing communication: Communication is key throughout both the buyer’s journey and the customer’s journey. Marketers need to maintain consistent communication with individuals to keep them engaged, informed and satisfied. Marketers can address questions, concerns and needs at each stage of the journey by establishing clear channels of communication.
Now that you are familiar with the similarities of customer journey vs buyer journey, it is important to understand their distinctions. Here are six differences between the buyer journey and the customer journey:
The buyer journey typically involves shorter timeframes, as customers are actively looking for information, comparing options and making a purchase decision. Businesses need to be strategic in their timing during the particular stage. It ensures that they are present and engaging with potential customers at the right moments to influence their decision-making process.
The customer journey involves longer timeframes, as it extends beyond the initial purchase to focus on building loyalty, providing support and encouraging repeat business. Timing is crucial in the stage as well, as businesses need to engage with customers, provide support and offer promotions.
Key takeaways:
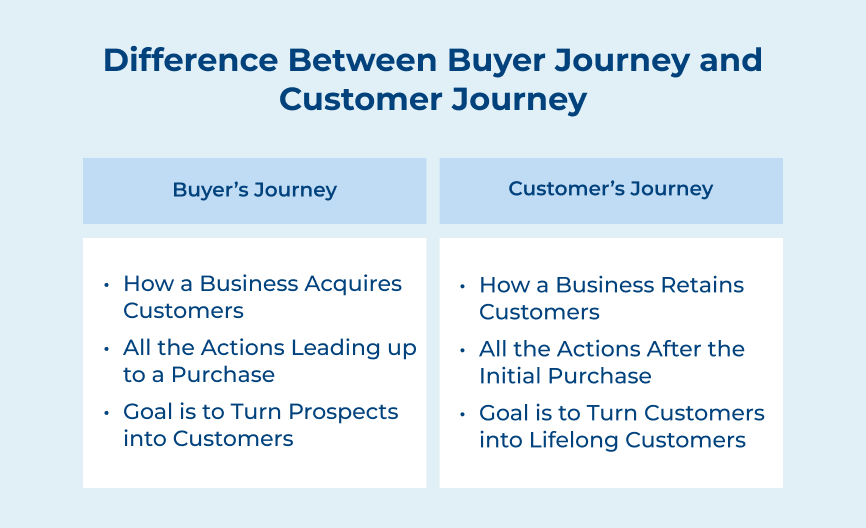
The buyer journey primarily focuses on the steps a person takes before making a purchase. It includes activities like research, comparison shopping and decision-making. The buyer journey is driven by the need to find the right product or service that meets the person’s needs and preferences.
The customer journey focuses on the steps a person takes after making a purchase. It includes activities like product usage, customer service interactions and loyalty building. The customer journey is driven by the need to provide a positive experience and build a long-term relationship with the customer.
Key takeaways:
The buyer journey focuses on the process a potential customer goes through before making a purchase. The journey typically includes awareness, consideration and decision stages. The touchpoints in the buyer journey are crucial moments where the customer interacts with the brand.
The customer journey continues after the purchase has been made. The journey focuses on retaining the customer and enhancing loyalty. The touchpoints in the customer journey can include post-purchase emails, customer support interactions and loyalty programs.
Key takeaways:
The primary goal in the buyer journey is to attract and convert potential customers into paying customers. It involves creating awareness, interest and consideration among the target audience to drive a purchase decision. The key goal in the buyer journey is to generate leads and convert them into customers.
The customer journey goal is to provide value, support and personalized experiences to customers to encourage loyalty. The key goal in the customer journey is to enhance customer satisfaction, increase retention rates and maximize customer lifetime value.
Key takeaways:
The focus in the buyer journey is primarily on metrics such as lead generation, website traffic and conversions. The metrics help businesses understand how well their marketing efforts are attracting potential customers and driving sales. The buyer journey is typically measured by tracking the number of leads generated, the conversion rate from lead to customer and the ROI of campaigns.
The customer journey focuses on metrics related to customer retention, satisfaction and loyalty. Businesses measure the customer journey by tracking metrics such as customer lifetime value, repeat purchases and customer satisfaction scores. The data helps businesses understand how well they are meeting the needs and expectations of their customers.
Key takeaways:
The key difference between the buyer journey and the customer journey lies in the concept of “lifecycle.” The buyer journey focuses on the stages a potential customer goes through before making a purchase, such as awareness, consideration and decision. It is essentially a pre-sale process that ends once a customer makes a purchase.
The customer journey encompasses the entire lifecycle of a customer’s interaction with a brand, from their initial purchase to becoming a loyal advocate for the brand.
Key takeaways:
The buyer’s journey involves understanding and catering to the needs of potential customers at each stage of their purchasing process. There are three main stages in the buyer’s journey, each with its own significance and implications for marketers.
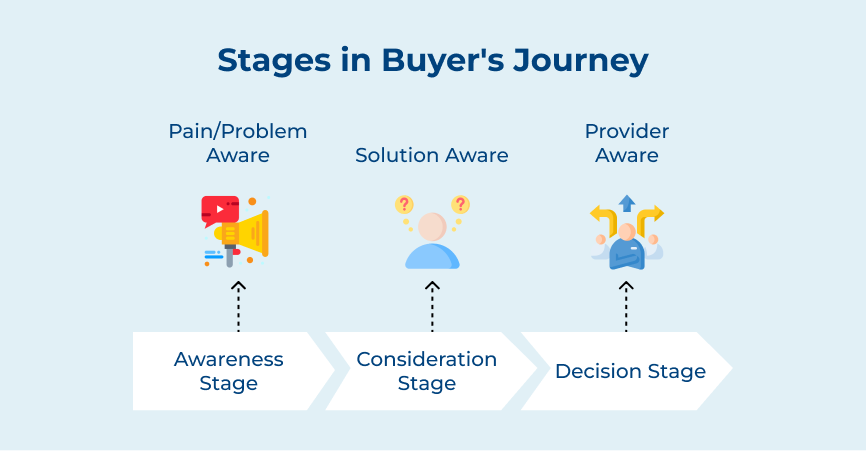
The awareness stage is the first step in the buyer’s journey, where a potential customer becomes aware of a problem or need that they have. It is the stage where a consumer recognizes that they have a pain point that needs to be addressed and they start researching various solutions.
The role of a marketer is to create content that educates the target audience about their problem and potential solutions. 83% of B2B content focuses on building brand awareness and interest.
Once a potential customer has identified their problem and gathered information about possible solutions in the awareness stage, they move on to the consideration stage. The consumer evaluates different options in the consideration stage. They also compare various products or services that could potentially solve their problem.
The consideration stage is where consumers are actively considering different options and are more open to exploring specific offerings. Providing relevant content can help marketers influence consumer perceptions and convince them that their product or service is the ideal choice.
The decision stage is the final step in the buyer’s journey, where the consumer is ready to make a purchase and choose a specific product or service provider. The role of a marketer is to facilitate decision-making and remove any barriers that might prevent the consumer from completing the purchase.
The decision stage is where the consumer converts into a customer and marketers must capitalize on the opportunity. Providing a seamless buying experience can help marketers secure the sale and create a loyal customer likely to make repeat purchases.
Businesses can better connect with their customers and drive sales by understanding the stages that accompany them. Check the key stages and how businesses can effectively navigate each stage to enhance the customer experience.
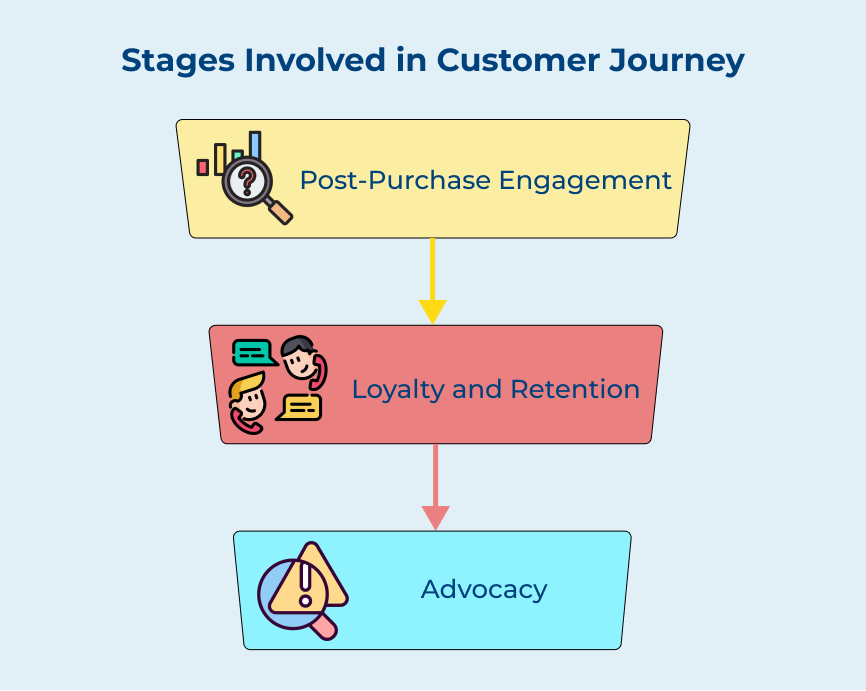
Post-purchase engagement is a crucial stage in the customer journey as it focuses on maintaining a positive relationship with customers after they have made a purchase. It involves following up with customers, addressing any concerns and encouraging them to provide feedback.
Some strategies for post-purchase engagement include sending thank-you emails, offering customer support through various channels and inviting customers to join loyalty programs. 90% of consumers say the post-purchase experience is just as important as the quality of the products.
Loyalty and retention are key objectives for businesses looking to build long-term relationships with customers. It focuses on incentivizing customers to continue purchasing from the business and rewarding them for their loyalty.
Strategies for enhancing loyalty include offering rewards programs, personalized discounts, exclusive offers and personalized communication. Businesses can increase customer satisfaction, reduce churn rates and create brand advocates by providing value to loyal customers.
Advocacy is the final stage in the customer journey and involves turning satisfied customers into brand advocates who promote the business to others. Brand advocates are customers who actively recommend the business to their friends, family and social networks. It helps to increase brand awareness and attract new customers.
Businesses can encourage advocacy by providing exceptional customer service, offering referral programs, showcasing customer testimonials and engaging with customers on social media. Creating a positive customer experience can help businesses turn loyal customers into powerful advocates. It helps to drive growth and success.
Understanding the difference between the buyer journey and the customer journey is essential for navigating the path to purchase effectively. The buyer journey focuses on the steps a potential customer takes to make a purchase, from awareness to consideration to decision. The customer journey extends beyond the purchase to focus on the ongoing relationship that a customer develops with a brand.
Businesses can tailor their marketing strategies to better meet the needs of their target audience by recognizing the distinct stages in both the buyer and customer journeys. Mapping out both journeys allows businesses to engage with customers at every stage of their buying process and beyond.
A customer is someone who purchases a product or service from a business, while a buyer is someone who acquires goods or services in exchange for money. The difference between the two is that a customer may not always be the one who makes the actual purchase, as buyers can purchase on behalf of others.
The buyer journey refers to the process a potential customer goes through before making a purchase, focusing on their experience and decision-making. The funnel represents the steps a customer takes from initial awareness to making a purchase, with stages like awareness, consideration and decision. The buyer journey is more holistic, while the funnel is more linear and focused on conversion.
Understanding the Buyer Journey and Customer Journey separately is important because they represent two distinct stages in the marketing process. The Buyer Journey focuses on the steps a potential customer takes before making a purchase. The Customer Journey focuses on the experience a customer has after making a purchase. Understanding and analyzing each journey separately can help businesses tailor their strategies to effectively engage with customers at every stage.
The buyer journey and customer journey are influenced by several factors. It includes demographics, psychographics, behavior and emotions. Other key factors include brand reputation, customer reviews, social proof and personalized messaging. The ease of purchasing, customer service and post-purchase experience also play a significant role in shaping the journey for consumers.
Businesses can optimize the Buyer Journey by focusing on attracting and converting leads into customers through targeted marketing. Optimizing the Customer Journey involves providing a seamless experience for existing customers to encourage loyalty. Both journeys are important for business success and should be tailored to meet the specific needs of each audience.
Market better, sell faster and support smarter with Veemo’s Conversation Customer Engagement suite of products.
Unify all your customer data in one platform to deliver contextual responses. Get a 360 degree view of the customer lifecycle without switching tools.
Connect with the tools you love to reduce manual activities and sync your business workflows for a seamless experience.
 https://veemo.io/wp-content/uploads/2025/12/customer-connection.png
1256
2400
Indrasish Singha
https://veemo.io/wp-content/uploads/2024/11/veemo.svg
Indrasish Singha2026-02-06 09:11:372026-01-19 09:14:05What is Customer Connection: Mistakes, Metrics & Examples
https://veemo.io/wp-content/uploads/2025/12/customer-connection.png
1256
2400
Indrasish Singha
https://veemo.io/wp-content/uploads/2024/11/veemo.svg
Indrasish Singha2026-02-06 09:11:372026-01-19 09:14:05What is Customer Connection: Mistakes, Metrics & Examples https://veemo.io/wp-content/uploads/2025/12/complaint-management.png
1256
2400
Indrasish Singha
https://veemo.io/wp-content/uploads/2024/11/veemo.svg
Indrasish Singha2026-02-03 09:04:022026-01-19 09:10:02What is Complaint Management? Importance, Key Steps & Strategies
https://veemo.io/wp-content/uploads/2025/12/complaint-management.png
1256
2400
Indrasish Singha
https://veemo.io/wp-content/uploads/2024/11/veemo.svg
Indrasish Singha2026-02-03 09:04:022026-01-19 09:10:02What is Complaint Management? Importance, Key Steps & Strategies https://veemo.io/wp-content/uploads/2025/12/AI-Self-Service.png
1256
2400
Indrasish Singha
https://veemo.io/wp-content/uploads/2024/11/veemo.svg
Indrasish Singha2026-01-26 09:52:482026-01-13 10:17:07What is AI Self Service? Benefits, Key Metrics and Best Practices
https://veemo.io/wp-content/uploads/2025/12/AI-Self-Service.png
1256
2400
Indrasish Singha
https://veemo.io/wp-content/uploads/2024/11/veemo.svg
Indrasish Singha2026-01-26 09:52:482026-01-13 10:17:07What is AI Self Service? Benefits, Key Metrics and Best PracticesGrow Customer Relationships and stronger team collaboration with our range of products across the Conversational Engagement Suite.
 Omnichannel Personalization: The What, Why and How
Scroll to top
Omnichannel Personalization: The What, Why and How
Scroll to top