1. Focus
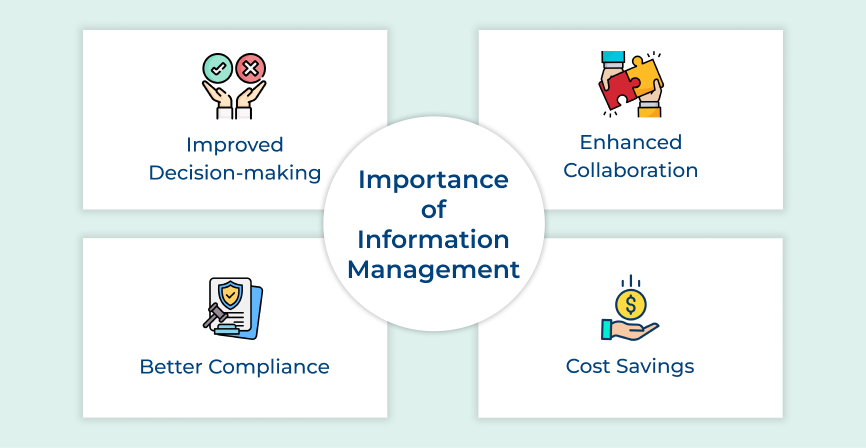
The key focus in information management is to systematically organize and ensure easy access to data. Information management aims to streamline processes related to storing and retrieving data, improving decision-making within an organization.
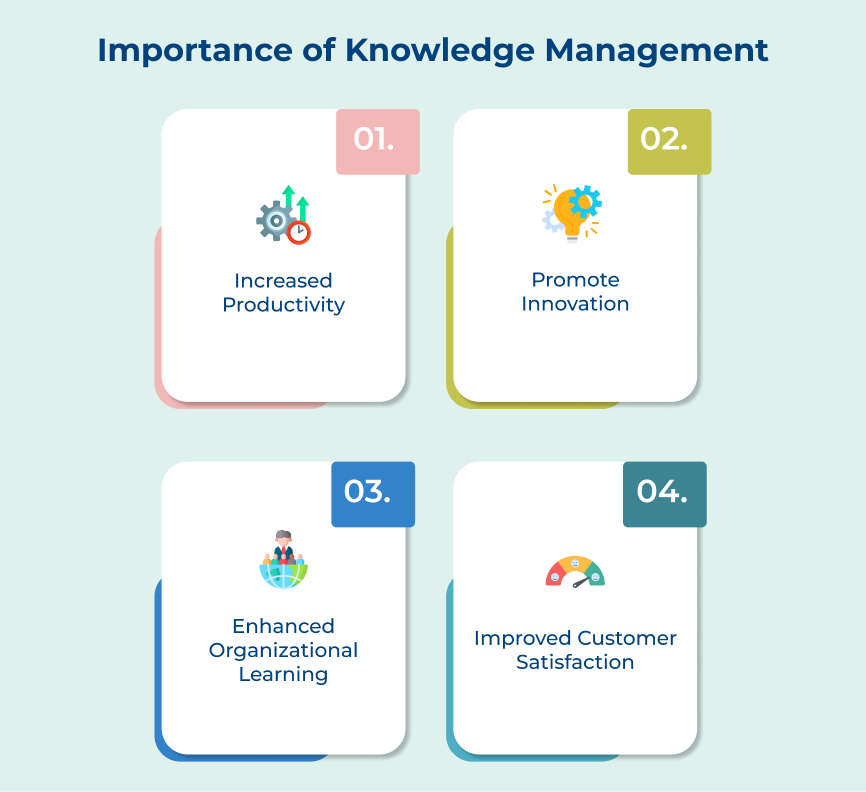
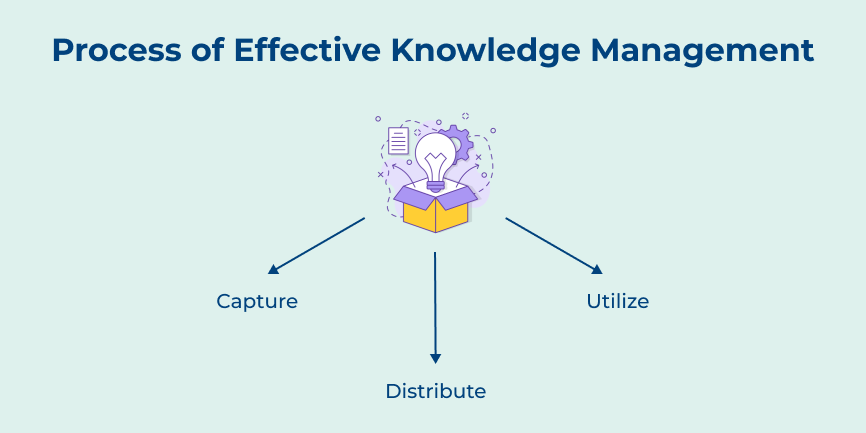
Knowledge management emphasizes leveraging the collective knowledge within an organization. The key takeaway here is the emphasis on creating a culture that promotes knowledge sharing, collaboration and innovation. Knowledge management seeks to harness the insights and expertise of employees to drive competitive advantage.
Key takeaways:
- Information management focuses on organizing and maintaining data, while knowledge management leverages collective expertise within an organization.
- Both disciplines are crucial for business success, emphasizing the need to manage information and knowledge effectively in an organization.
2. Purpose
Information management focuses on organizing, storing and retrieving data systematically. The purpose of information management is to ensure that information is easily accessible and properly maintained for quick problem-solving. It involves the management of data, documents and records within an organization to improve workflow.
Knowledge management is more concerned with capturing, sharing and using knowledge to enhance organizational performance. The purpose of knowledge management is to promote innovation, collaboration and learning within a company by leveraging the experiences of employees. It involves the creation of a knowledge-sharing culture, the development of knowledge repositories and the implementation of knowledge-sharing tools.
Key takeaways:
- Information management aims to streamline processes, reduce clutter and improve access to data for more efficient operations.
- Knowledge management focuses on innovation and collaboration, aiming to leverage the collective knowledge of employees to drive growth.
3. Types of Information/Knowledge
Information management deals with structured data that is stored in databases, documents and other systems. It focuses on managing information that is objective and can be easily categorized.
Knowledge management deals with unstructured knowledge that is subjective and based on individual experiences. It focuses on capturing and sharing tacit knowledge that is often difficult to codify.
Key takeaways:
- Knowledge management involves capturing and sharing expertise to enhance productivity within a company.
- Knowledge management focuses on enhancing a learning culture for employee growth, development and retention of intellectual capital.
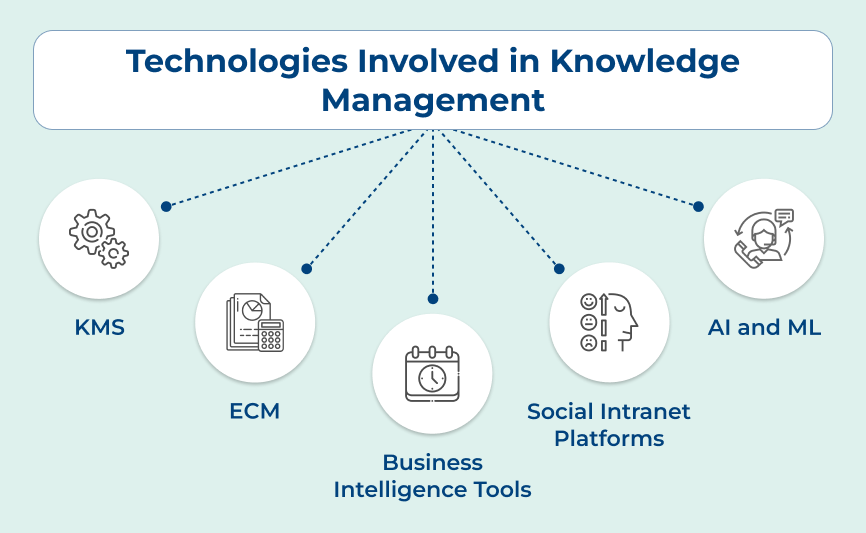
4. Tools and Technologies
Tools in information management mainly focus on storing data like databases, content management systems, document software and analytics tools. The tools help in the collection, storage, retrieval and manipulation of data to ensure it is easily accessible.
Knowledge management tools are geared towards capturing, sharing and leveraging knowledge within an organization. It includes knowledge bases, collaboration software, social networking platforms and expertise location systems. The tools facilitate knowledge sharing, collaboration and learning within an organization to improve decision-making.
Key takeaways:
- Information management tools can centralize data storage and streamline information retrieval processes.
- Knowledge management tools promote collaboration and knowledge sharing among employees, promoting a culture of continuous learning.
5. Ownership
Ownership in information management refers to maintaining and updating databases, documents, or records. The ownership is usually assigned to a specific individual or team within an organization, making them accountable for the accuracy and accessibility of the information.
Ownership in knowledge management is more about the intellectual property and expertise held by individuals within an organization. Knowledge is often considered to belong to the person who possesses it, rather than to the organization as a whole. Individuals may be reluctant to share their intellectual property, causing challenges in capturing and sharing valuable knowledge.
Key takeaways:
- Clear ownership roles and responsibilities are essential in information management to ensure that data is accurate.
- Enhancing a culture of knowledge sharing in knowledge management can help overcome barriers to sharing valuable expertise and insights.
6. Impact
Information management primarily helps in making decisions based on data and facts. It allows for quick access to information, which can improve efficiency and productivity. The impact of information management is limited to data and may not spur innovation or strategic decisions.
Knowledge management has a deeper impact on an organization. Applying knowledge can enhance innovation, improve problem-solving capabilities and enhance overall performance. Knowledge management encourages collaboration and learning within teams, leading to a more dynamic organizational culture.
Key takeaways:
- Information management in terms of impact is improved decision-making based on data and increased efficiency in managing information.
- Knowledge management has a more transformative impact due to its focus on leveraging collective intelligence and expertise.
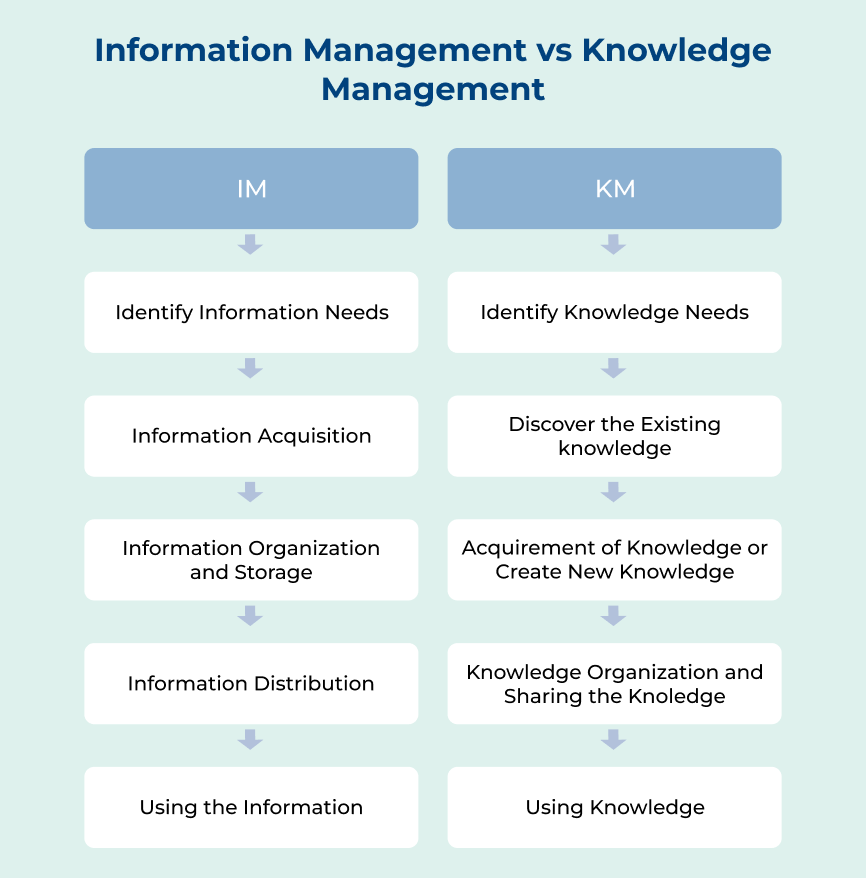
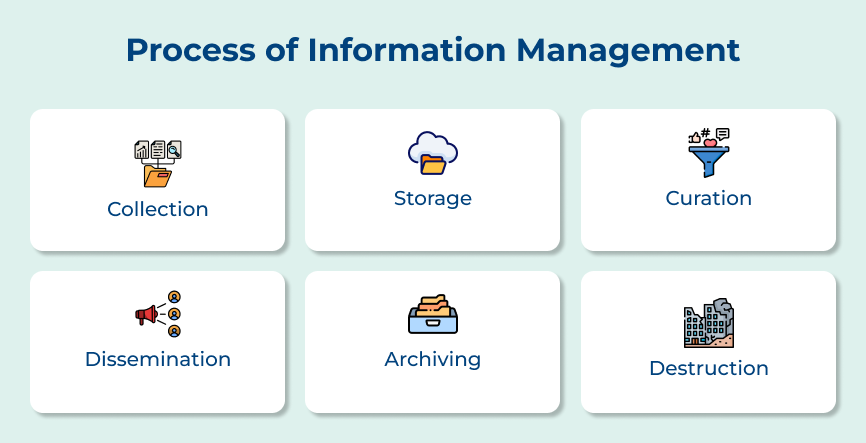
Process of Effective Information Management
Check out the critical steps for mastering information management that can vastly improve operational efficiency and decision-making in any setting.