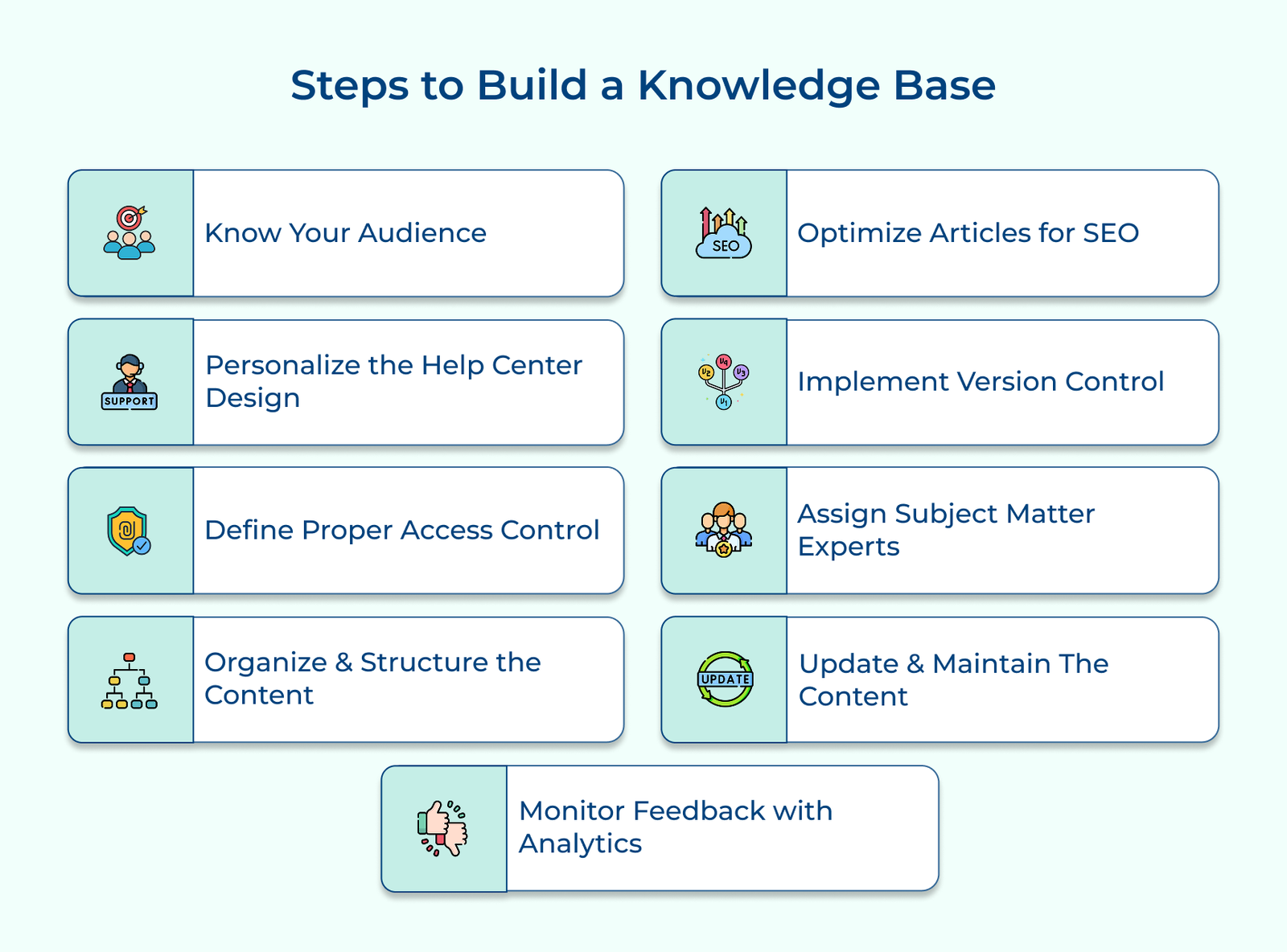
#1 Know and Understand the Target Audience
Before initiating the process of building a knowledge base, it’s critical to have a clear understanding of who the target audience is. Consider their demographics, needs, and preferences to tailor the knowledge base content. It will ensure that the information provided is relevant and valuable to your audience.
Having a deep understanding of the target audience helps to create content that addresses their pain points, provides solutions to their problems, and improves their overall customer experience. A well-defined target audience allows brands to target the content, making it more engaging and user-friendly.
Best Practices:
- Conduct market research and customer surveys to gather insights into the target audience’s preferences.
- Use analytics tools to analyze the behavior and interests of your audience on the website.
- Continuously refine the knowledge base content based on feedback and user interactions to ensure it remains relevant.
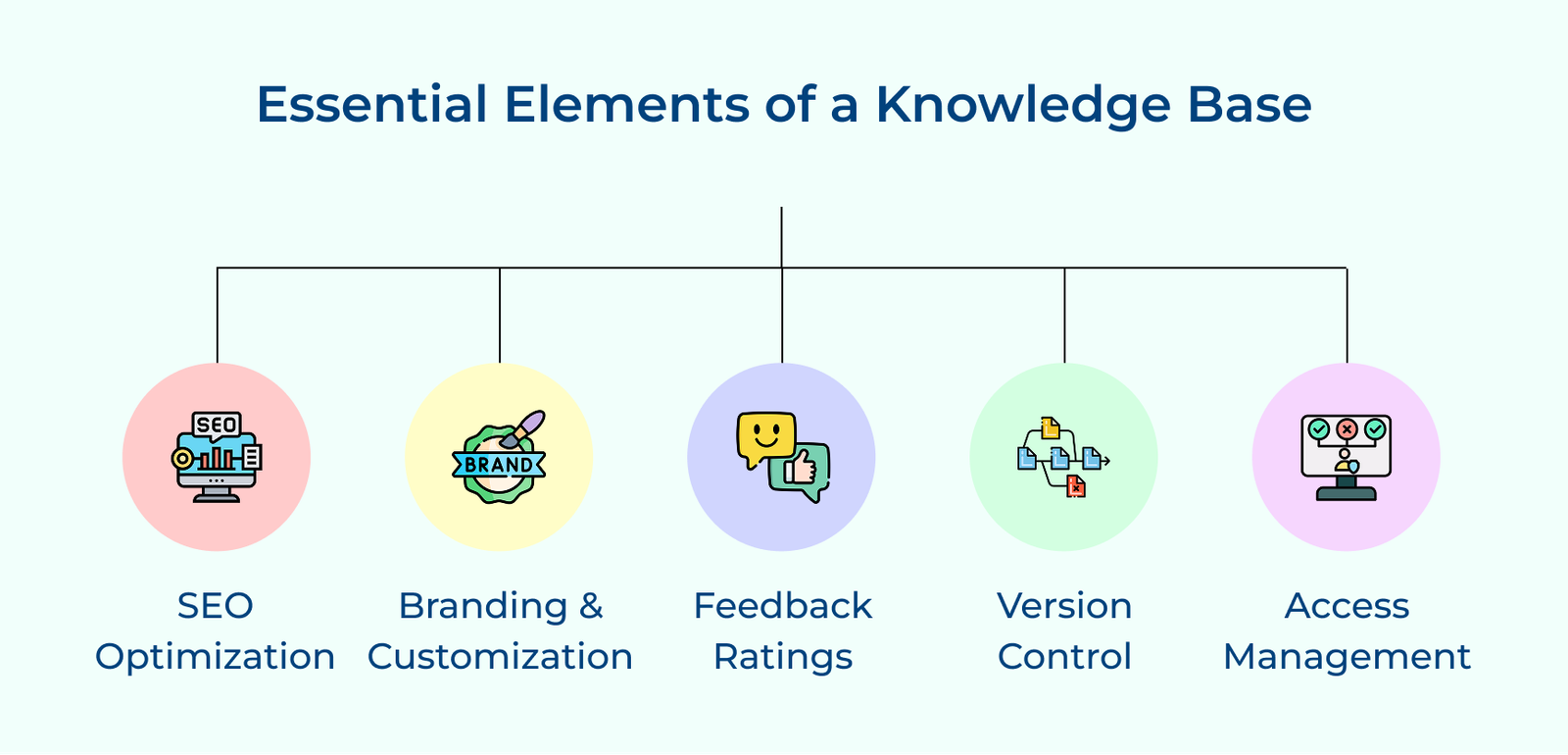
#2 Personalize Help Center Design to Match the Branding
More than 70% of customers feel frustrated when website content is not personalized. Personalizing the design of the help center helps create a sense of familiarity and continuity for the customers. Businesses create a seamless transition from their website to the help center by incorporating the brand colors, logo and overall visual identity.
A personalized help center design allows businesses to showcase their brand’s personality and values. The brand is more than just a logo or color scheme; it is a representation of what the business is as a brand. The personal touch can go a long way in building strong customer relationships and promoting brand loyalty.
Best practices:
- Ensure the design elements of the help center, such as colors, fonts, and imagery, align with your overall branding.
- Design a user-friendly interface with intuitive navigation that allows customers to find the information they need. Well-organized categories, search functionality, and clear labeling contribute to a positive user experience.
- Incorporate visually appealing graphics, images and videos that not only capture attention but also effectively communicate the brand’s message.
#3 Define Proper Access Control Management
Access control management refers to the process of defining and enforcing access restrictions to protect sensitive data within the knowledge base. A knowledge base often contains highly confidential data. Implementing access controls ensures that only authorized individuals can access the information.
Access control also helps maintain the integrity of the knowledge base. Unauthorized users may modify or delete crucial data without proper controls, leading to inaccuracies. Companies can preserve the reliability and credibility of the knowledge base by enforcing access restrictions.
Best practices:
- Assign specific roles to users based on their responsibilities and grant access privileges accordingly. The users only have access to the information relevant to their roles.
- Implement monitoring and logging systems to keep track of user activities within the knowledge base.
- Periodically review and update access permissions to align with organizational changes. Regular audits also help identify and mitigate potential security risks.
#4 Organize and Structure Your Content
Once there’s a clear understanding of the target audience, it’s time to structure and organize your knowledge base effectively. Divide the information into categories, topics, or sections that make it easy for users to navigate and find what they are looking for. Consider using a logical and intuitive hierarchy or taxonomy system.
Creating a knowledge base that is well-organized boosts the user experience by enabling users to quickly find the information they need. It eliminates confusion and frustration, improving customer satisfaction.
Best Practices:
- Use clear headings, subheadings and labels to categorize your content. Make sure to keep them descriptive as well.
- Employ a search function that allows users to find specific information quickly.
Create a user-friendly interface with clear navigation menus and an intuitive design.
#5 Optimize Articles for SEO
SEO-optimized articles help improve the visibility and ranking of the knowledge base in search engine results. When users search for relevant keywords, search engines like Google prioritize websites that are optimized for SEO. It leads to higher organic traffic and increased exposure.
Having high visibility in search engines will attract more visitors to the knowledge base, allowing the company to establish itself as a trusted source of information. Optimizing for SEO also improves the user experience by making articles more user-friendly, with clear headings, meta descriptions and relevant keywords.
Best practices:
- Conduct keyword research to identify popular search terms related to your content. Integrate the keywords naturally into your article’s title, headings and body.
- Craft compelling meta-tags and descriptions for the articles, as they can greatly impact click-through rates. Include relevant keywords and a concise summary of the article’s content.
- Producing valuable, well-researched content that solves users’ problems not only attracts more readers but also encourages other websites to link back to your articles.
#6 Implement Version Control
Version control helps prevent errors by providing a systematic way to track and manage changes made to the knowledge base. It allows multiple contributors to work simultaneously while keeping track of their revisions, making it easier to identify and resolve conflicts.
Implementing version control also promotes collaboration among team members by facilitating communication and sharing of ideas. It provides a centralized platform where team members can contribute their expertise, review and maintain a unified vision of the knowledge base.
Best practices:
- Establish a central location of the knowledge base to ensure that all team members have a single source of truth and reduce the risk of fragmentation.
- Regularly review and test any modifications before committing them to the main knowledge base.
- Implementing version control helps in addressing any issues that may arise, as well as in maintaining the credibility of the knowledge base.
#7 Assign Subject Matter Experts and Contributors
Organizations should first identify subject matter experts within their team or industry and assign them specific areas of expertise for contributing to the knowledge base. Subject matter experts (SMEs) possess deep knowledge and expertise in specific areas, which allows them to provide reliable information for the knowledge base.
Topic contributors bring diverse perspectives and insights to the knowledge base. They can offer different approaches and solutions to problems, which results in promoting innovation. Companies can manage a more comprehensive and well-rounded knowledge base by involving a wider group of contributors..
Best practices:
- Identify and involve subject matter experts from different departments or teams to ensure a comprehensive knowledge base.
- Establish clear guidelines for contributors to ensure consistent and high-quality content.
- Foster a collaborative culture that encourages and rewards contributions to the knowledge base, creating a sense of ownership among employees.
#8 Update and Maintain Your Content Regularly
An effective knowledge base is not a one-time effort; it requires regular updates and maintenance to remain relevant. Continuously refining the content maintains its accuracy and keeps it in line with the evolving industry trends.
Regular maintenance prevents outdated or incorrect information from being accessed by users, avoiding confusion and potential frustrations. It also addresses emerging customer concerns, introduces new products or features, and incorporates best practices into the knowledge base.
Best Practices:
- Assign dedicated individuals or teams responsible for regularly reviewing and updating the knowledge base.
- Establish a feedback loop with users to gather insights, identify gaps and address any user-reported issues promptly.
- Continuously train and educate the employees on knowledge base management processes to ensure they know how to contribute effectively.
#9 Monitor Feedback with Knowledge Base Analytics
Measuring customer feedback helps brands identify gaps in their existing knowledge base. Regularly reviewing customer comments, queries and suggestions can highlight areas where information may be missing or unclear. Businesses can enhance the overall quality and completeness of their knowledge base, ensuring that customers can access the information they need.
Knowledge base analytics allows businesses to identify patterns and trends in customer inquiries. Its data can provide valuable insights into the most common issues or topics that customers are seeking assistance with. Brands can prioritize the creation of new content or update existing articles to address such FAQs.
Best practices:
- Set aside dedicated time to review and analyze feedback data on a regular basis. It keeps brands updated on customer needs and trends.
- Apply sentiment analysis techniques to understand the overall sentiment of the feedback received. It helps to categorize feedback as positive, negative, or neutral.
- Encourage customer participation by actively seeking their feedback and opinions. It can be done through surveys, pop-up questionnaires, or feedback forms.
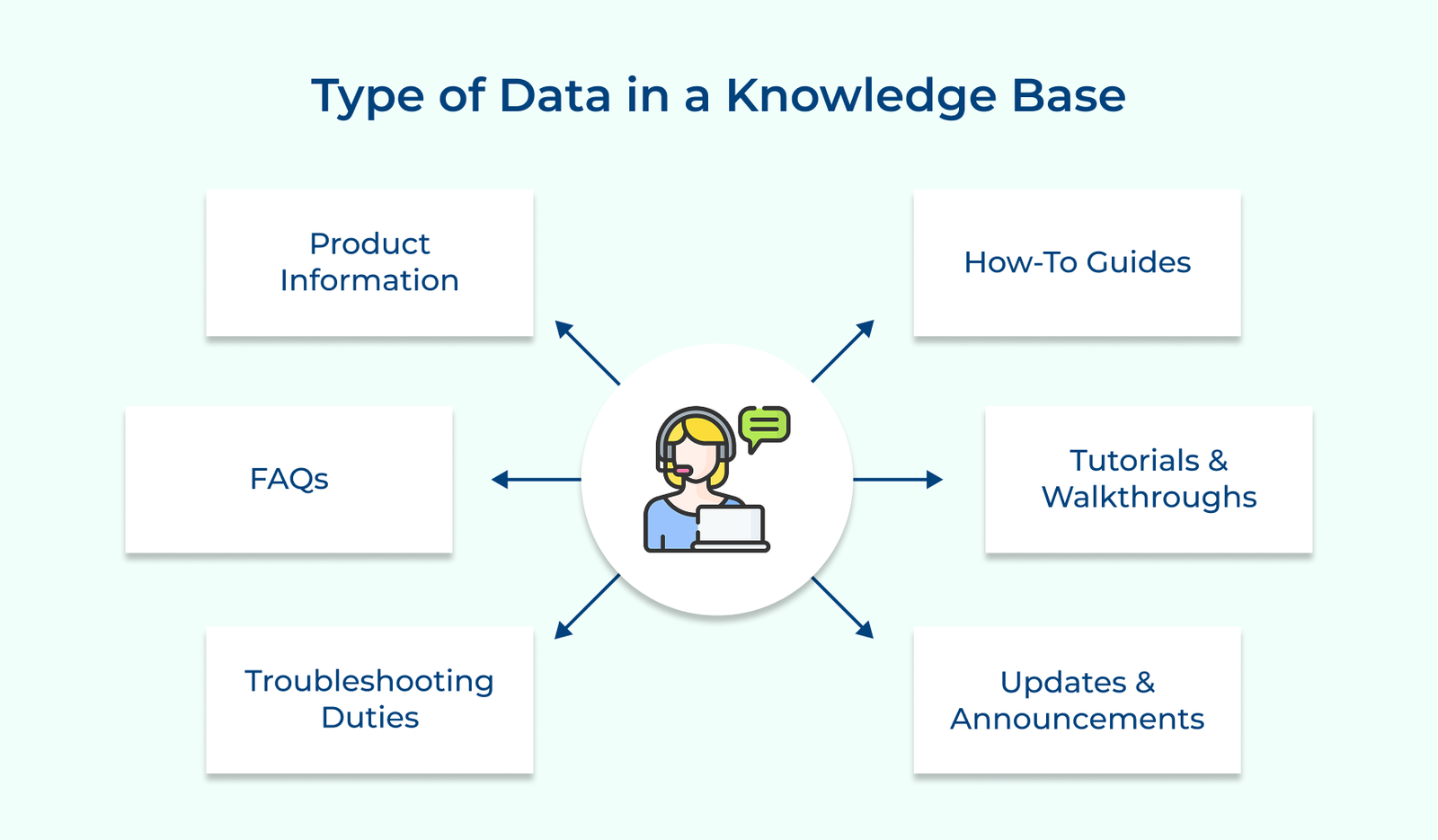
What Type of Data is Included in a Knowledge Base?
Below are the various data types found in a knowledge base and how each contributes to improved user experiences and informed decision-making.