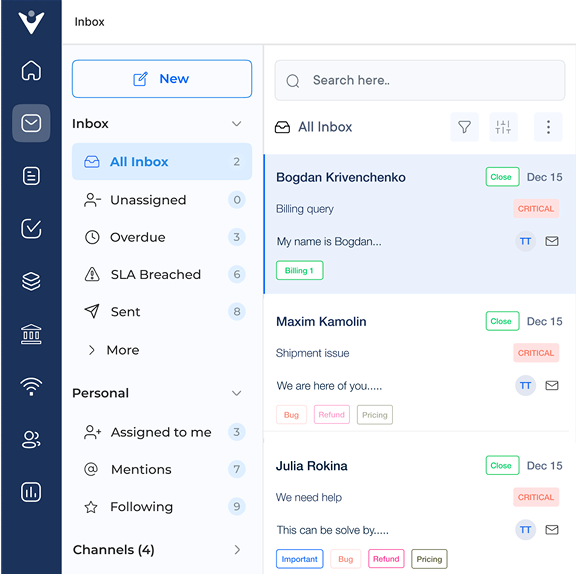
1. Incident Logging
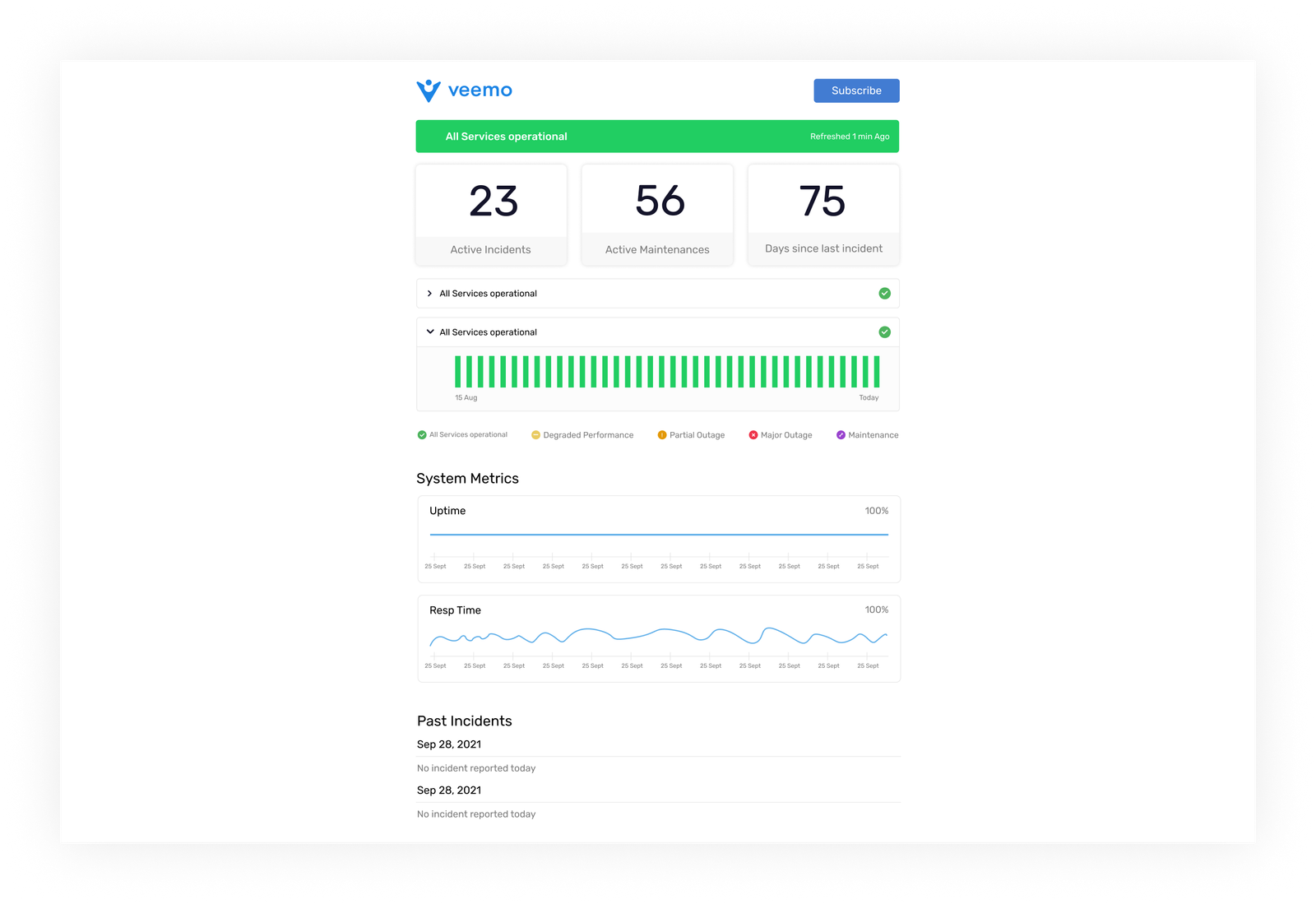
Incident logging is a crucial step in the IT incident management process. It includes documenting incident details such as timing, reporter identity and impact on business operations. The process is vital as it helps track and manage incidents effectively, ensuring a quick resolution.
Let’s imagine a company experiencing a server outage. Logging incident details such as time and user reports helps IT assets. It minimizes disruption to business operations while restoring the server.
Pro tips:
- Standardize the incident logging process to ensure consistency and accuracy in recording incident details.
- Include a severity level classification to prioritize incidents based on their impact on the business.
- Implement a centralized incident logging system to facilitate easy access and retrieval of incident information for analysis.
2. Incident Categorization
Incident categorization is an essential step in the IT incident management process. It involves identifying the incident based on its impact, urgency and technical details. IT teams can quickly determine the severity of the issue and take appropriate actions. Critical incidents are prioritized to minimize disruptions to business operations.
Let’s assume a situation where incident categorization during a server outage helps identify high-priority issues. It needs immediate attention from lower-priority ones for IT maintenance.
Pro tips:
- Clearly defined categorization criteria to ensure consistency in incident classification.
- Regular training for IT staff on incident categorization practices to improve accuracy and efficiency.
- Utilizing incident management tools that automate the categorization process to save time and increase productivity.
3. Incident Prioritization
Incident prioritization is a crucial step in the IT incident management process. It involves evaluating the severity of an incident to determine the order in which it should be addressed. Prioritizing incidents can ensure that the most critical issues are addressed first, minimizing downtime and impact on business operations.
A use case for incident prioritization could be a scenario where a major system outage occurs, affecting multiple users. Consider a case where the IT team would need to prioritize the incident over less critical issues. It minimizes the impact on business operations and customer service.
Pro tips:
- Clearly defining criteria for prioritization, such as severity, impact and urgency.
- Regularly reviewing and updating incident priorities based on changing circumstances.
- Communicating effectively with stakeholders to ensure alignment on incident priorities and expectations.
4. Incident Assignment
Incident assignment is a crucial step in the IT incident management process. The step involves assigning an incident to a specific individual or team responsible for resolving it. Assigning incidents accurately can ensure an effective response to incidents, minimizing downtime and disruption to operations.
The step also helps in establishing accountability for incident resolution and tracking progress toward resolution. A use case scenario could be when a critical system goes down. The incident assignment step ensures that the incident is assigned to the relevant team of system administrators. It ensures quick troubleshooting and resolves the issue to minimize the impact on business operations.
Pro tips:
- Clearly define responsibilities and escalation paths to ensure incidents are assigned to the right individuals or teams.
- Use automated tools for incident assignment to streamline the process and improve efficiency.
- Regularly update assignment rules and criteria to ensure incidents are assigned based on priority.
5. Task Creation and Management
Task creation and management is a crucial step in the IT incident management process. It involves documenting tasks that need to be completed to resolve the incident at hand. Breaking down the incident into smaller tasks allows for delegation, progress tracking and efficient resolution.
Let’s consider it in the event of a network outage. The tasks could include diagnosing the issue, contacting the internet service provider and implementing a solution to restore connectivity.
Pro tips:
- Prioritize tasks based on impact and urgency to ensure that critical issues are addressed first.
- Assign tasks to team members with the relevant skills and expertise to expedite the resolution process.
- Regularly update the status of tasks and communicate progress to stakeholders to maintain transparency.
6. SLA Management and Escalation
SLA management and escalation are crucial steps in the IT incident management process. SLA management involves monitoring service level agreements with customers or stakeholders. It ensures that incidents are resolved within agreed-upon timeframes. Incidents not resolved within SLAs escalate to higher support levels or management for resolution.
The steps help in the incident management process by providing clear guidelines for resolving issues promptly and maintaining productivity. Let’s assume if a critical system outage occurs, SLA management and escalation processes can help prioritize the incident. It allocates resources effectively and communicates updates to stakeholders.
Pro tips:
- Establish clear communication channels for reporting and escalating incidents to ensure quick response times.
- Regularly update SLAs to ensure they align with business priorities and customer expectations.
- Document and track incident resolution processes to identify areas for improvement.
7. Incident Resolution
Incident resolution is a critical step in the IT incident management process where the IT team works to resolve the issue at hand quickly and efficiently. It involves identifying the root cause of the incident and implementing a solution.
Incident resolution helps in the incident management process by minimizing downtime and reducing the impact on business operations. Imagine a server has gone down. The IT team will work quickly to identify the issue and implement a solution to get the server back online. It ensures minimal disruption to the company’s services.
Pro tips:
- Keeping all stakeholders informed throughout the resolution process can help manage expectations and ensure everyone is on the same page.
- Keeping detailed records of the incident, including the steps taken to resolve it, can help in future incident management and troubleshooting.
- After the incident is resolved, it’s important to review what happened, what worked well and what can be improved for future incidents.
8. Incident Closure
Incident closure is the final step in the IT incident management process. The incidents here are resolved, documented and closed out. Incident closure is essential for recording incidents, their resolutions and lessons learned in incident management. Properly closing out incidents can improve the overall incident response strategies and prevent similar incidents from occurring in the future.
A use case for incident closure would be when a server outage occurs within a company. The IT team would work to resolve the issue, document the actions taken and close out the incident once normal operations have been restored.
Pro tips:
- Ensure all documentation is up to date and accurate for future reference.
- Conduct a post-mortem analysis to identify root causes and potential improvements.
- Communicate the closure of the incident to all relevant stakeholders to provide transparency and maintain trust.
Roles and Responsibilities Involved in IT Incident Management
Following is the breakdown of the critical roles in IT incident management, ensuring you’re equipped with the knowledge to contribute effectively and streamline your organization’s incident response efforts.