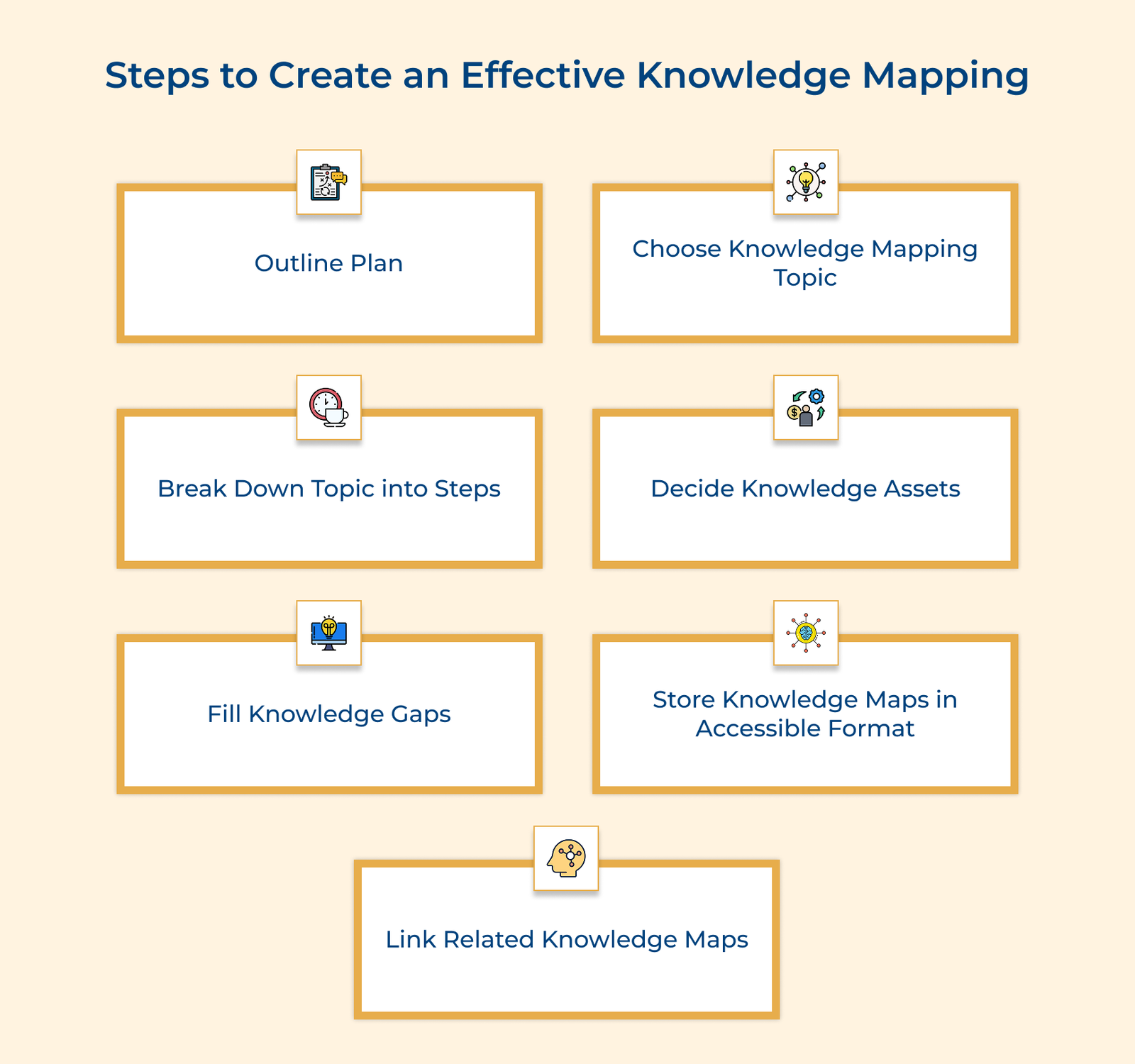
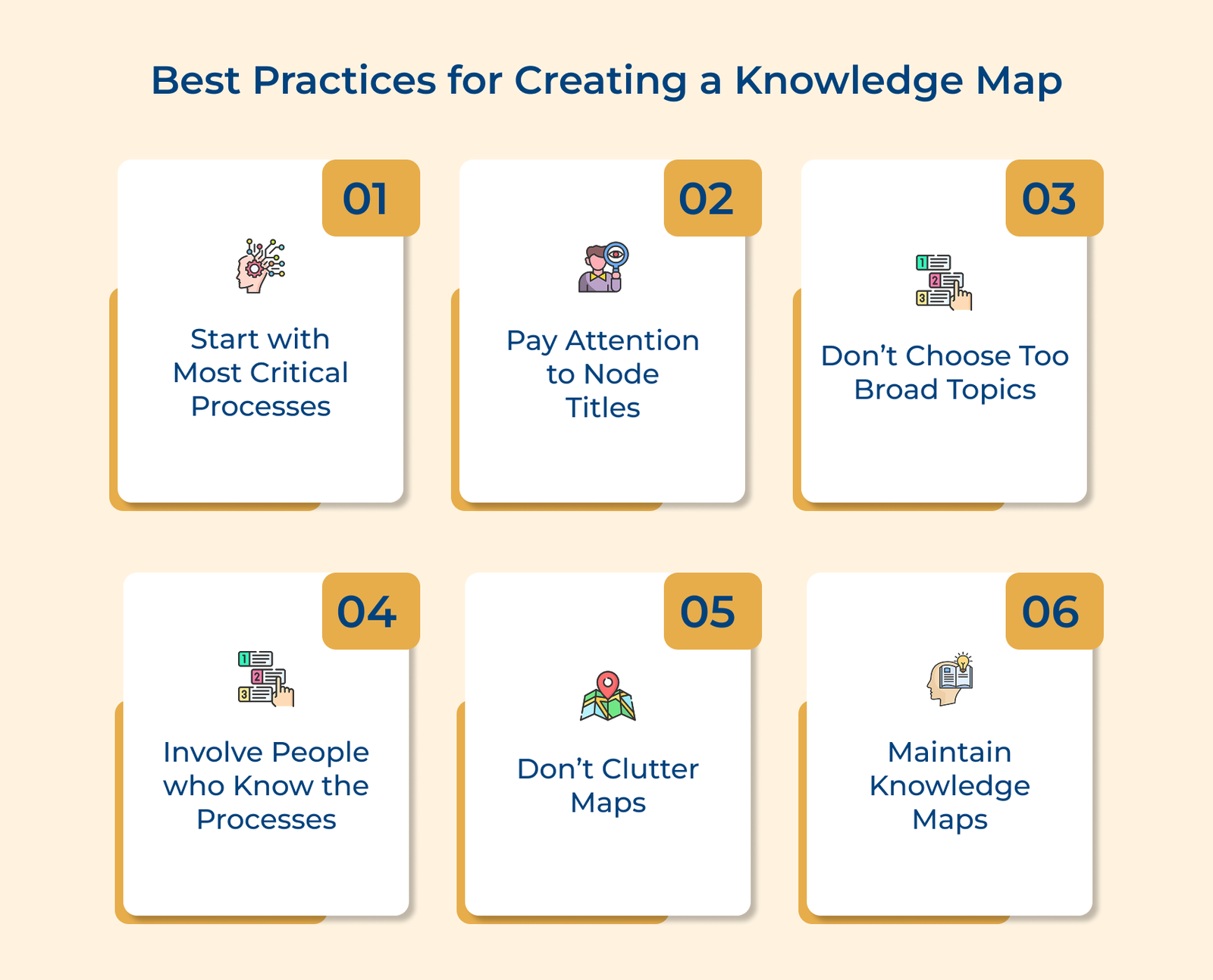
1. Outline the Plan
Knowledge mapping is a crucial process for organizing and visualizing information within an organization. Start by determining the scope and objectives of the mapping project. Identify key stakeholders and their roles in the process to ensure buy-in. Set a timeline with clear milestones to track progress and keep the project on schedule.
Best practices:
- Clearly define the purpose of the knowledge mapping project to guide decision-making and ensure alignment with organizational objectives.
- Engaging with stakeholders early to gather input, address concerns and ensure their needs are met throughout the process.
- Regularly reviewing progress against milestones and adjusting the plan as needed to stay on track.
2. Choose the Knowledge Mapping Topic
Consider factors like revenue generation, customer satisfaction, operational efficiency and risk mitigation. Focus on processes or departments where improved knowledge flow can lead to significant gains. Align the topic selection with organizational goals and strategies. Identify knowledge areas that directly support key objectives, such as increasing market share or enhancing employee skills.
Consider existing knowledge management initiatives when selecting the topic. Look for opportunities to complement or expand upon current efforts, such as document management systems or expert directories. Integrating the knowledge map project with established practices can increase its effectiveness and buy-in.
Pro tips:
- Engage leadership to help identify high-priority topics and secure resources.
- Analyze data from various sources (e.g., performance metrics, employee feedback) to inform topic selection.
- Choose a topic that allows for quick wins to build momentum and demonstrate value.
3. Break the Topic Down into Necessary Steps
Break the chosen topic down into smaller, manageable steps to create an effective knowledge map. Decompose the subject matter into specific tasks, processes, or knowledge areas. It could involve mapping out the stages of a customer journey, the components of a product development cycle or the key skills required for a particular job role. As you break down the topic, identify dependencies and relationships between the various elements.
Let’s consider if you’re mapping the customer onboarding process, you might break it down into steps like initial contact, needs assessment, solution presentation and account setup. Each step would have associated knowledge, such as product information, pricing guidelines and legal requirements, with clear connections between them.
Pro tips:
- Use mind mapping or outlining tools to visually organize the breakdown.
- Iterate and refine the breakdown as you gather more information.
4. Decide what Knowledge Assets are Needed
When creating an effective knowledge mapping, it is crucial to decide what knowledge assets are needed to support the goals. Start by identifying existing knowledge sources such as documents, experts and databases within the organization. Assess the relevance and accuracy of the knowledge assets to ensure they align with the mapping objectives.
Determine if there is a need for new knowledge assets to fill any gaps in the current resources. It may involve conducting research, conducting interviews with subject matter experts, or creating new documentation.
Best practices:
- Use tools: Utilize technology tools such as knowledge management systems or mapping software to streamline the identification and organization of knowledge assets.
- Review and update: Regularly update the knowledge assets to ensure they remain current and aligned with the mapping objectives.
5. Fill in the Knowledge Gaps
Creating an effective knowledge map requires filling in knowledge gaps by capturing tacit knowledge from subject matter experts, organizing information and verifying the knowledge. Tacit knowledge, which is the expertise and insights held by individuals, is crucial for a comprehensive knowledge map.
Experts should be interviewed and their knowledge documented. Relevant information from various sources, such as documents and websites, should be gathered in a structured manner. The collected knowledge must then be validated and verified to ensure accuracy.
Key Benefits:
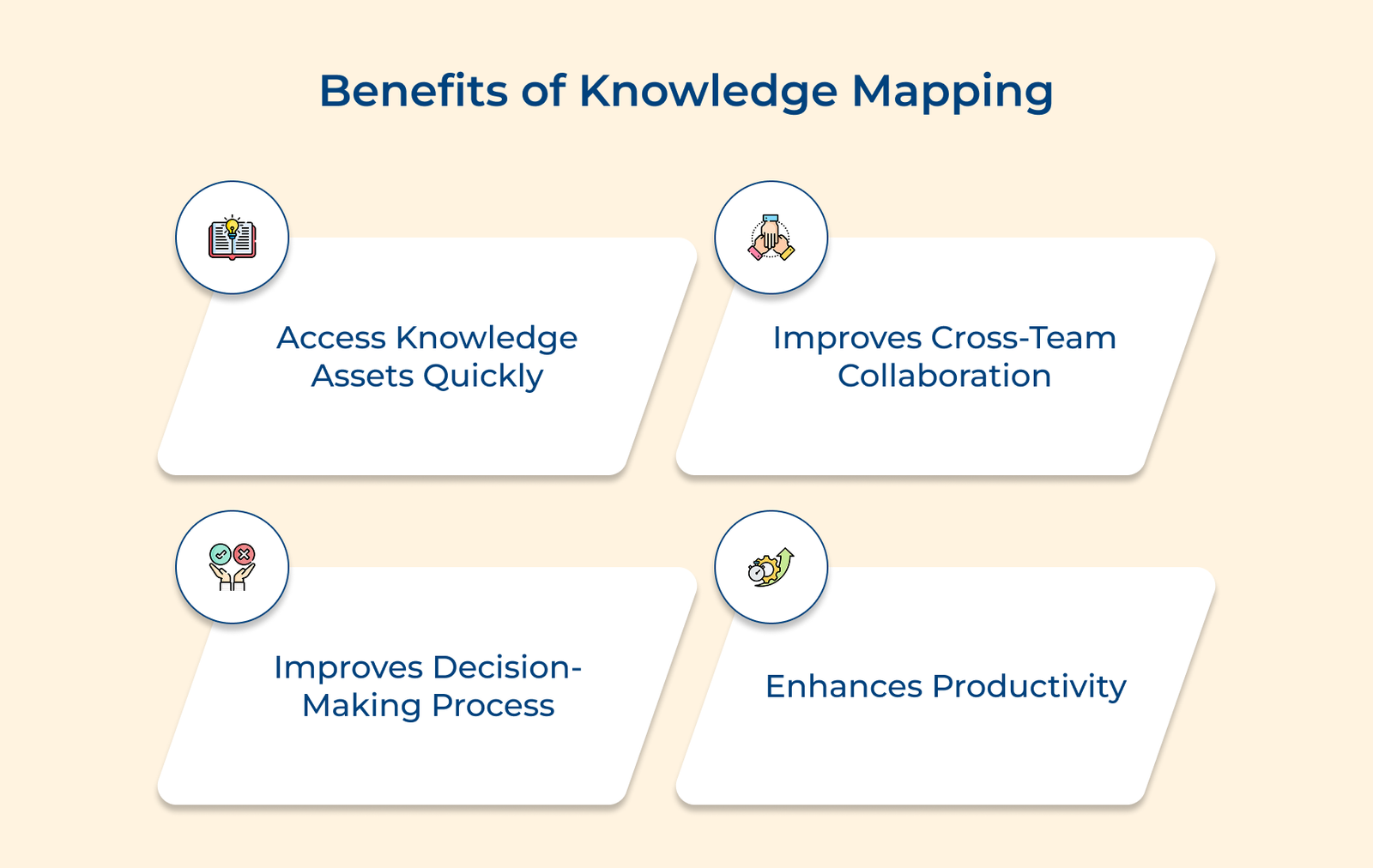
- Improved decision-making: A complete and accurate knowledge map enables better-informed decisions by providing access to critical information.
- Increased efficiency: Employees can quickly find the information they need, reducing time wasted searching for answers and reinventing the wheel.
6. Store the Knowledge Maps in an Accessible Format
Storing the knowledge maps in an accessible format is a crucial step in creating an effective knowledge mapping system. It involves choosing an appropriate knowledge management system that aligns with the organization’s needs and goals. The system should be user-friendly, enabling employees to easily navigate and access the information they require.
Implementing effective search and retrieval mechanisms is another critical aspect of the step. The knowledge management system should have powerful search capabilities, allowing users to quickly find relevant information using keywords, tags, or categories. It should also support different file formats and enable easy updating of the knowledge maps.
Importance of it:
- Enhanced knowledge sharing: An accessible knowledge mapping system promotes a culture of knowledge sharing, encouraging employees to contribute and collaborate.
- Better knowledge retention: Storing knowledge maps in a centralized, accessible format can help mitigate the risk of losing valuable knowledge when employees leave or retire.
7. Link Related Knowledge Maps Together
Linking related knowledge maps together is an essential step in creating an effective knowledge mapping system. Establishing connections and relationships between various knowledge maps, can create a comprehensive knowledge network that facilitates knowledge sharing. The interconnectedness allows users to navigate seamlessly between related topics, discover new insights and understand the bigger picture.
Pro tips:
- Use metadata and tags: Assign relevant metadata to each knowledge map, making it easier to identify and link related content.
- Implement a consistent naming convention: Develop a standardized naming convention for the knowledge maps to ensure clarity and consistency. It makes it easier for users to understand the relationships between different maps and navigate the knowledge network.
- Regularly review and update connections: As new knowledge maps are created or existing ones are updated, regularly review and update the connections between them. It ensures that the knowledge network remains accurate, relevant and up-to-date.
5 Popular Knowledge Mapping Tools
Let us now go through the five popular knowledge mapping tools to help you visually organize and structure information.
1. Veemo Support