1. Implement Multi-factor Authentication (MFA)
Multi-factor Authentication (MFA) is a crucial security measure requiring users to provide two or more verification factors for access. Around 1 in 4 companies have turned to MFA after a cybersecurity breach. MFA typically combines something the user knows (like a password) with something they have (such as a smartphone) or something they are (like biometric data).
Types of MFA include SMS-based codes, authenticator apps and biometric verification. SMS MFA sends a one-time code to the user’s phone, while authenticator apps generate time-based codes on the device. Biometric MFA relies on unique physical traits, such as fingerprints or facial recognition.
Actionable tips:
- Prioritize high-risk accounts: Implement MFA first for accounts that access sensitive data or critical systems.
- Educate users on benefits: Provide clear instructions and highlight the security advantages of MFA to encourage adoption.
- Offer multiple options: Give users the flexibility to choose from various MFA methods, balancing security with convenience.
2. Provide Regular Security Training for Customer Service Staff
As threats evolve, employees must stay informed about the latest risks and best practices. Regular training enhances a security-conscious culture and equips staff to respond to potential threats effectively.
Given that phishing and social engineering often target customer service representatives with access to sensitive information, the training is essential. Methods can include interactive workshops, online courses, simulated phishing exercises and discussions of real-world scenarios.
Pro tips:
- Schedule regular training sessions: Hold monthly or quarterly security updates to keep staff informed about new threats.
- Use diverse formats: Combine e-learning modules, in-person workshops and hands-on exercises to accommodate various learning styles.
- Test and reinforce knowledge: Conduct periodic assessments and provide incentives for top performers to encourage ongoing learning.
3. Use Secure Communication Channels
Encryption safeguards intercepted communications, keeping personal and financial data safe from unauthorized access. Implement chat and voice systems with end-to-end encryption for all interactions, including internal staff communications.
The systems should also offer automatic message deletion, secure file transfer and robust identity verification for all participants.
Actionable tips:
- Audit current communication channels: Identify and replace any unsecured systems with encrypted alternatives.
- Empower your team with secure communication: Train employees on using encrypted channels and verifying customer identities to enhance security.
- Stay ahead with regular updates: Keep your systems up-to-date with the latest encryption standards to safeguard your operations.
4. Develop and Enforce Strong Password Policies
Strong passwords are your first line of defense. They should be long, complex or unique for each account, blending uppercase along with lowercase letters, numbers and special characters. Using password managers can simplify the process, allowing staff to generate and securely store robust passwords without memorizing them.
Periodically checking passwords against breach databases and prompting immediate changes when necessary can further protect your business from cyber threats. The proactive approach ensures that your business reduces the risk of unauthorized access.
How to implement:
- Create a password strength meter: Give users instant feedback while they create or update their passwords.
- Encourage passphrases: Teach your team to use memorable, longer phrases instead of complicated passwords for better security.
- Automate compromised password checks: Implement tools that regularly scan and alert users about any potentially compromised credentials.
5. Implement Role-based Access Control (RBAC)
Role-Based Access Control (RBAC) is a powerful way to limit system access to authorized users based on their specific roles within your organization. RBAC upholds the principle of least privilege by ensuring that employees only access the information essential for their jobs, reducing the risk of data breaches and unauthorized actions.
Start by identifying the various roles within your team and defining the appropriate access levels for each. Let’s consider that a junior representative may have limited access to customer data, while a team leader might enjoy broader privileges. Regularly adjusting access rights is crucial to keep them aligned with evolving roles.
Actionable tips:
- Conduct a comprehensive role analysis: Outline all roles within your customer service team and define their necessary access levels.
- Implement a gradual RBAC rollout: Begin with a pilot group to pinpoint and resolve any issues before full implementation.
- Establish a regular review process: Schedule quarterly reviews of access rights to ensure they match current roles and responsibilities.
6. Encrypt Sensitive Customer Data
Key information that should be encrypted includes personal identification details, financial records, health information and any confidential customer data. Encryption should safeguard both data at rest (stored in databases or files) and data in transit (being transmitted over networks).
There are several encryption methods available, including symmetric and asymmetric encryption. Compliance with regulations like GDPR, HIPAA and PCI DSS often necessitates specific encryption standards. Staying informed about the requirements and implementing robust encryption methods that meet or exceed them is crucial for data security.
Pro tips:
- Identify and categorize sensitive data: Develop a comprehensive data inventory to ensure all sensitive information is securely encrypted.
- Use strong encryption algorithms: Implement industry-standard encryption methods, such as AES for data at rest and TLS for data in transit.
- Manage encryption keys securely: Establish strict protocols for key generation, storage and rotation to protect the integrity of your encrypted data.
7. Conduct Regular Security Audits and Assessments
Security audits are vital for spotting vulnerabilities and ensuring your security measures are effective. There are two primary types: internal audits conducted by your IT security team and external audits by third-party firms.
The frequency of the assessments varies based on regulatory requirements and the sensitivity of your data, but annual audits are standard practice. Key areas to evaluate include network security, access controls, data encryption, employee practices and incident response procedures.
Best Practices:
- Develop a comprehensive audit checklist: Create a detailed list that covers all aspects of customer service security for thorough evaluations.
- Combine automated and manual testing: Utilize security tools for automated scans while also performing manual reviews to catch any issues that automated tools might overlook.
- Act on audit findings promptly: Prioritize and address identified vulnerabilities swiftly, tracking progress to ensure all issues are resolved.
8. Establish a Secure Remote Work Environment
Creating a secure environment for off-site customer service representatives is essential with the rise of remote work. Secure remote access solutions, like Virtual Private Networks (VPNs), establish encrypted tunnels for data transmission, protecting information even on public Wi-Fi networks.
Ensure all work devices are equipped with up-to-date antivirus software, firewalls and security patches. Monitoring remote activities can help detect unusual patterns that may signal a security breach, using tools like logging systems, regular check-ins and performance monitoring.
Actionable tips:
- Provide company-managed devices: Issue work-specific laptops or mobile devices with pre-configured security settings for optimal protection.
- Implement a clear remote work policy: Establish guidelines for secure data handling, approved software use and incident reporting procedures to ensure consistency.
- Use remote monitoring tools: Deploy solutions that track device health, security status and user activities while respecting privacy.
9. Implement AI-powered Fraud Detection Systems
The systems can quickly analyze patterns, detect anomalies and flag suspicious activity with greater speed than human agents alone. They effectively identify various fraud types, including identity theft, account takeovers and unusual transaction patterns.
AI systems should be set up to alert human operators for final decision-making on complex or high-stakes issues. The approach prevents legitimate activities from being mistakenly flagged as fraudulent while preserving the essential human touch in customer service.
Best practices:
- Start with a pilot program: Launch AI fraud detection on a small scale to refine the system before full deployment.
- Continuously train the AI model: Regularly update the system with new data to enhance accuracy and keep pace with evolving fraud tactics.
- Establish clear escalation procedures: Clearly define when and how AI-flagged issues should be escalated for human review.
10. Create and Maintain an Incident Response Plan
Key elements include clear definitions of what constitutes an incident, step-by-step response procedures and a communication strategy for internal along with external stakeholders. The plan should be thorough yet adaptable to various security incidents.
Clearly defining roles and responsibilities is essential for a coordinated response. It involves identifying who will lead the effort, manage communications and handle technical remediation. Regular testing and updates ensure the plan remains relevant against evolving threats.
Actionable tips:
- Conduct regular tabletop exercises: Simulate different incident scenarios to evaluate the plan’s effectiveness and team readiness.
- Establish a clear chain of command: Define decision-making authority and communication channels to eliminate confusion during an incident.
- Create pre-approved communication templates: Prepare draft messages for various stakeholders to ensure swift and consistent communication in the event of an incident.
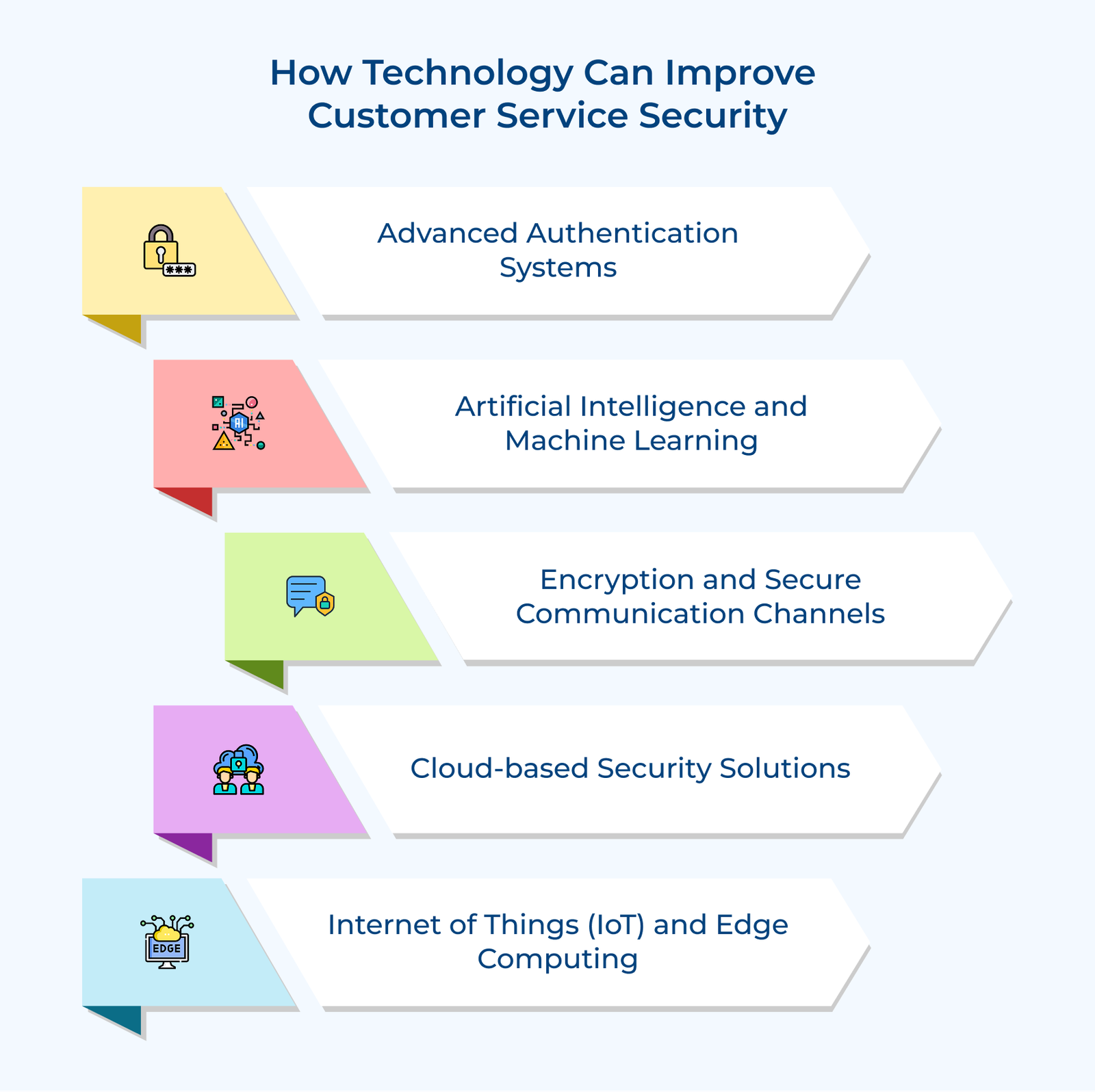
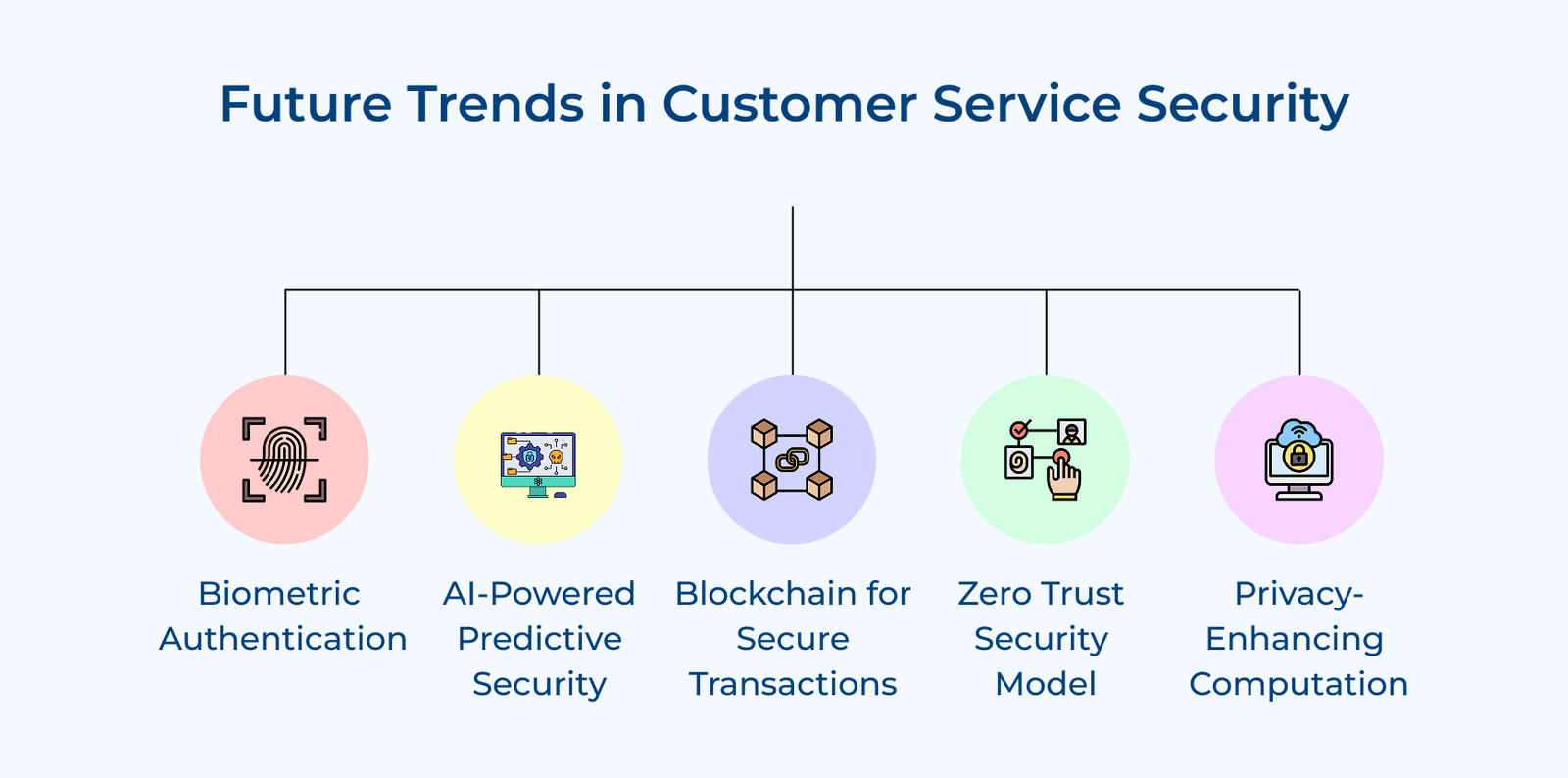
How Technology Can Improve Customer Service Security
Here’s how technology can significantly enhance the security of your customer service operations and provide a stronger defense against cyber threats: