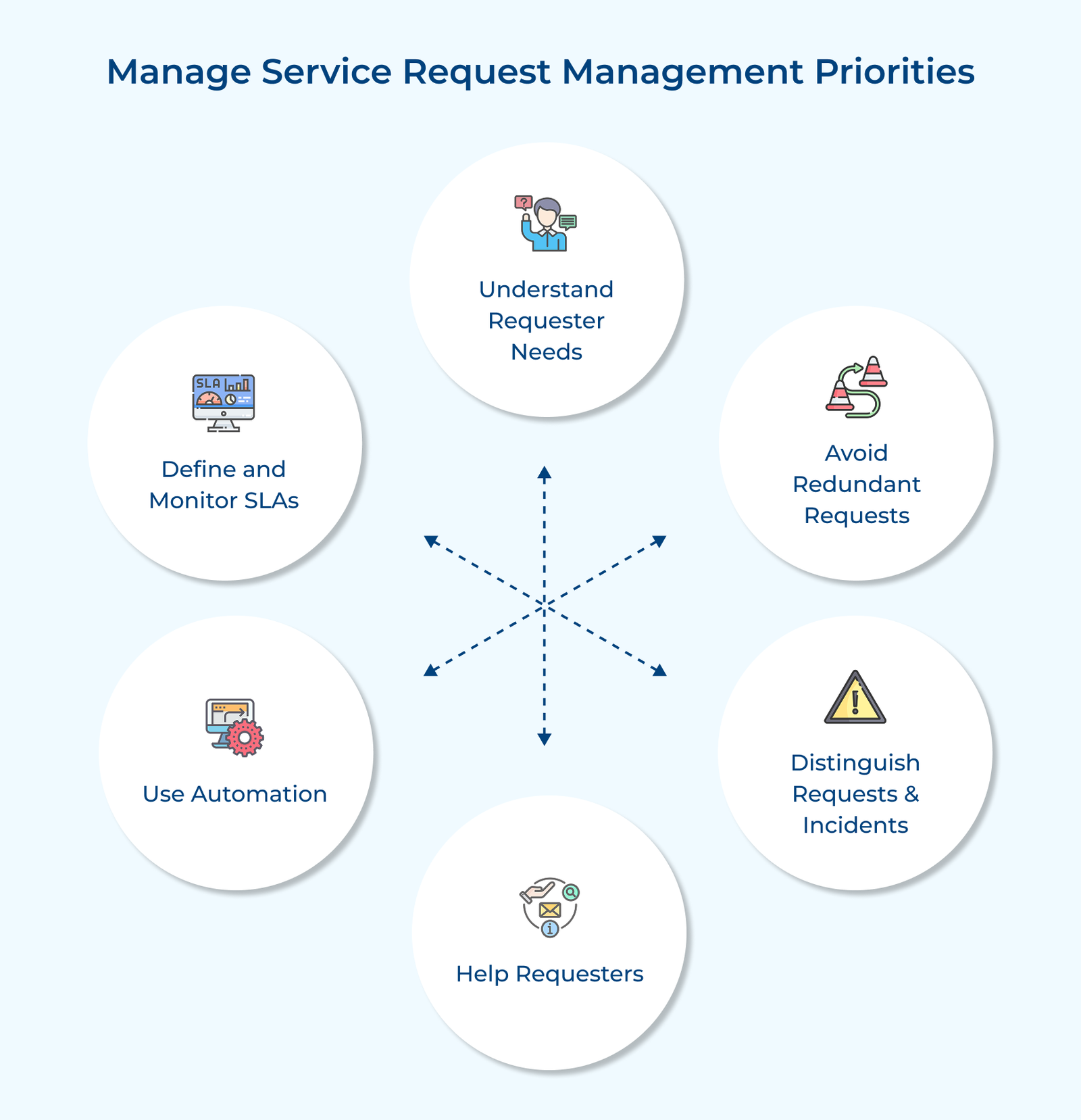
1. Understand Requester Needs
Understanding requester needs is crucial for effective service request management prioritization. It involves establishing clear communication channels to facilitate seamless interactions with requesters. It could include dedicated email addresses, web portals, or helpdesk systems.
Gathering detailed information about the request is essential to accurately assess its nature, scope and potential impact. The information should include a clear description of the request, any supporting documentation and the desired timeline from the requester’s perspective.
Best practices:
- Developing standardized request intake forms or templates to ensure consistent information gathering.
- Providing training to service desk staff on effective communication and requester needs assessment.
- Regularly reviewing and updating prioritization criteria to align with evolving business needs.
2. Avoid Redundant Requests
Redundant requests not only waste valuable resources but also contribute to inefficiencies and frustration among requesters. Implementing request deduplication processes involves establishing mechanisms to identify and consolidate similar or duplicate requests. It can be achieved through techniques such as keyword matching or leveraging machine learning algorithms to detect redundancies.
Providing visibility into request status is another crucial step in minimizing redundant requests. They are less likely to submit duplicate requests due to a lack of visibility or communication by keeping requesters informed about the progress of their requests.
Best practices:
- Maintaining a comprehensive knowledge base or self-service portal, where requesters can search for solutions before submitting a request.
- Implementing automated notifications or status updates to keep requesters informed about the progress of their requests.
- Conducting regular audits and analyzing request data to identify patterns of redundancy.
3. Distinguish Requests from Incidents
Requests have distinct characteristics and require different handling approaches. Defining the difference between requests and incidents is the first step. Requests typically involve planned activities, such as access provisioning, or changes to existing services. Incidents are unplanned disruptions or issues that require immediate attention, such as system outages, security breaches, or performance degradation.
Let’s consider that if an employee requests a software upgrade, it would be categorized as a request and follow the standard deployment process. If the same employee reports an application crash, it would be classified as an incident and escalated to the appropriate support team for immediate resolution.
Pro tips:
- Developing comprehensive categorization guidelines and decision trees.
- Implementing robust ticketing or service management tools with built-in request and incident classification capabilities.
- Conducting knowledge-sharing sessions to reinforce the distinction and ensure consistent categorization practices.
4. Help Requesters Help Themselves
Empowering requesters with self-service options is an effective strategy for managing service request management priorities. Organizations can reduce the volume of routine requests, freeing up resources to focus on more critical and complex tasks by providing self-help resources. Offering self-help resources, such as frequently asked questions (FAQs), step-by-step tutorials and instructional videos, can further enhance the self-service experience.
The resources should be regularly updated and cover a wide range of topics relevant to the requesters’ needs. Let’s assume that an IT service desk could offer a self-service portal where employees can reset their passwords or troubleshoot common technical issues using documented solutions.
Pro tips:
- Conducting user research to ensure the self-service portal is intuitive and user-friendly.
- Continuously expanding the self-help knowledge base based on frequently asked questions and common request patterns.
- Promoting and encouraging the use of self-service options through targeted communication campaigns.
5. Use Automation to Manage Repetitive Tasks
Utilizing automation to manage repetitive tasks is a powerful strategy for streamlining service request management priorities. Organizations can significantly improve efficiency by identifying recurring request patterns and automating their fulfillment. Identifying recurring request patterns is the first step in this process. Once the patterns are identified, organizations can implement automation scripts to handle the requests.
Leveraging chatbots or virtual assistants can further enhance the automation experience by providing requesters with a conversational interface to submit and track requests. The AI-powered assistants can guide users through the request process, gather necessary information and trigger automated workflows for fulfillment.
Best practices:
- Continuously monitoring request data to identify new automation opportunities and refine existing workflows.
- Ensuring proper testing and validation of automated processes to maintain accuracy.
6. Define and Monitor Service Level Agreements (SLAs)
Defining and monitoring service level agreements (SLAs) is crucial for prioritizing service request management effectively. SLAs establish clear expectations and timelines for addressing requests based on their priority levels. Setting realistic SLAs for each priority level is essential.
Let’s assume that critical requests may have an SLA of 2 hours for initial response and 8 hours for resolution. Low-priority requests could have an SLA of 24 hours for response and 5 business days for resolution. An example from a recent study by HDI revealed that organizations with well-defined SLAs experienced a 25% reduction in missed deadlines and a 20% increase in customer satisfaction rates.
Best practices:
- Involving stakeholders from various departments to ensure SLAs align with business needs and operational capabilities.
- Explain requester about the SLA process and inform them about the priority level set of their request to keep them updated
Difference Between Service Request Management and Incident Management
Let’s dive in to learn about the key differences between the two essential components of IT service delivery.