What is Knowledge Transfer: A Comprehensive Guide
Explore the concept of knowledge transfer, its importance in organizations, effective strategies for implementation and the benefits of enhancing a culture of continuous learning in organizations.

Explore the concept of knowledge transfer, its importance in organizations, effective strategies for implementation and the benefits of enhancing a culture of continuous learning in organizations.

Organizations face a significant challenge as valuable knowledge walks out the door with departing employees. The loss of expertise can result in decreased productivity, costly mistakes and missed opportunities. Without effective knowledge transfer, teams waste time reinventing the wheel, new hires struggle to find their footing and projects stall.
There’s a solution! You can capture, preserve and share essential information throughout your organization by implementing a strategic knowledge transfer plan. Let’s dive in to understand how businesses use it effectively to drive growth in a constantly evolving landscape.
Knowledge transfer refers to the process of sharing expertise, skills and information within an organization. It involves a systematic approach to capturing, organizing and distributing knowledge, ensuring that valuable insights are preserved effectively. It includes formal methods like training sessions, documentation and mentoring, alongside informal approaches such as team collaborations.
The process involves identifying key knowledge, selecting the best sharing methods and implementing strategies for effective transfer. Technology plays a vital role, with knowledge management systems and collaborative platforms serving as essential tools for disseminating information.
Key objectives:
Let’s delve into why knowledge transfer is a cornerstone for sustainable growth and success.
1. Preserves Organizational Expertise
Knowledge transfer safeguards critical information and skills when employees depart. Organizations can preserve institutional memory by capturing and sharing the expertise of experienced staff, ensuring operational continuity. The approach enables companies to build on past successes rather than starting new with each project or challenge.
2. Enables Faster Onboarding and Skill Development
An effective knowledge transfer plan accelerates the learning curve for new employees. When knowledge is organized and easily accessible, new hires can quickly gain the skills they need to become productive team members. The approach not only saves time and resources on training but also boosts confidence from day one.
3. Facilitates Innovation
Knowledge transfer enhances innovation by encouraging the exchange of ideas and best practices across departments. When diverse perspectives come together, they spark new insights, drive creative problem-solving and lead to enhanced processes.
4. Supports Succession Planning and Leadership Development
Knowledge transfer is essential for nurturing future leaders, providing them access to the wisdom and strategic insights of their predecessors. The continuity in leadership knowledge enhances organizational stability and facilitates smoother transitions during key personnel changes.
5. Enables Data-driven and Informed Choices
When knowledge is effectively transferred and easily accessible, decision-makers at all levels can draw on a wider array of information. It results in more informed, data-driven decisions that are likely to deliver better outcomes for the organization.
6. Promotes a Culture of Continuous Learning and Improvement
Implementing strong knowledge transfer processes enhances a culture of continuous learning and development across the organization. It creates an environment where sharing insights and learning from one another is the norm, promoting personal growth. The culture of improvement keeps the company agile to changing market conditions and new opportunities.
When evaluating or implementing a knowledge transfer program, there are six key elements to look for that indicate a robust and effective system:
An effective knowledge transfer program should have clear goals and measurable outcomes aligned with the organization’s strategic objectives. It should specify what knowledge needs to be shared, who will receive it and the timeline for transfer. Establish clear metrics for success, such as enhanced productivity, shorter training times or increased innovation.
The program should feature a structured framework to guide the transfer process, ensuring consistency and thoroughness. It must remain flexible to accommodate different learning styles and various types of knowledge. Striking a balance between formal methods (training sessions, documentation) and informal approaches (mentoring, on-the-job learning) is key to its success.
Seek initiatives that encourage subject matter experts to participate willingly and create a supportive environment where learners feel comfortable asking questions. Programs that promote two-way dialogue are typically more successful than those with a one-directional flow of information.
Good knowledge transfer programs harness technology to streamline sharing and access to information. It can involve knowledge management systems, collaborative platforms or e-learning tools. The technology should be user-friendly and accessible, enhancing the transfer process rather than complicating it.
The program should be integrated into the organization’s existing workflows, complementing other HR processes like performance management, succession planning and career development. It ensures that the knowledge transfer plan becomes a natural part of the organizational culture rather than an added burden.
A robust knowledge transfer program includes mechanisms for continuous assessment and improvement. It should feature feedback loops that enable participants to share their insights, along with regular reviews to identify areas for enhancement. It ensures the program remains relevant and effective as the organization’s needs evolve.
We’ll explore eight effective strategies that can elevate your ability to teach, mentor and share knowledge with confidence.

Organizations create a single source of truth for all critical information by implementing centralized databases. The databases should be well-organized, easily searchable and regularly updated, allowing employees to quickly access what they need.
Collaborative platforms enhance the system by enabling real-time sharing and updates. Tools like wikis, intranets and project management software empower employees to contribute knowledge, ask questions or collaborate on documents. It enhances a dynamic environment where knowledge is actively shared and continuously improved.
Pro tips:
Mentorship programs are an effective way to transfer tacit knowledge—the expertise that’s hard to document but vital for success. Organizations can facilitate the sharing of skills, insights and culture in a personalized way by pairing experienced employees with newcomers.
Mentorship is crucial to set clear goals and expectations to ensure mentorship programs are effective. Both mentors and mentees should understand their objectives, if it’s developing specific skills, mastering company processes or navigating career paths. Regular check-ins or feedback sessions will help keep the program on track and ensure it provides value to both parties.
Pro tips:
Comprehensive documentation is vital for preserving and transferring explicit knowledge within an organization. Detailed process guides offer step-by-step instructions for complex tasks, ensuring consistency and minimizing errors. The guides should be clear and include visual aids to enhance understanding.
Keeping standard operating procedures (SOPs) up-to-date is equally essential. SOPs provide a standardized approach to routine operations, ensuring all employees adhere to best practices. Regular reviews and updates are necessary to reflect changes in processes, technologies or regulatory requirements.
Pro tips:
Cross-training programs rotate employees through different roles or departments, exposing them to various aspects of the organization. The approach transfers knowledge across the business and cultivates a more versatile workforce.
Cross-training helps employees grasp how different parts of the organization connect by encouraging skill diversification. It can enhance problem-solving, as diverse perspectives come together to tackle challenges. Cross-training boosts job satisfaction by offering variety and growth opportunities.
Pro tips:
Technology is essential for modern knowledge transfer strategies. Video conferencing and webinars enable real-time knowledge sharing across distances, making it easy to conduct training sessions, expert panels or Q&A sessions for a wide audience.
Implementing internal social networks enhances a more informal, continuous knowledge-sharing environment. The platforms allow employees to ask questions, share insights and collaborate on projects in a familiar, social media-like setting, effectively encouraging the transfer of knowledge across different generations.
Actionable tips:
Enhancing a culture that prioritizes continuous learning is crucial for effective transfer of knowledge. One effective way to do the step is by integrating knowledge sharing into performance evaluations, signaling that learning and teaching are valued skills.
Recognizing and rewarding knowledge transfer efforts can further strengthen the culture. It might include formal awards for outstanding mentors or knowledge contributors and informal shout-outs in team meetings or company newsletters.
Actionable tips:
Regular knowledge audits help organizations pinpoint critical knowledge areas and identify potential gaps. The process involves assessing existing knowledge assets to determine where essential information may be at risk of loss.
Once gaps are identified, organizations can implement targeted knowledge transfer initiatives, such as developing specific training programs, enhancing mentorship relationships or documenting processes that depend on individual expertise.
Actionable tips:
Storytelling is a powerful tool for knowledge transfer, making complex ideas relatable and memorable. Sharing experiences through narratives conveys not just facts but also context, emotions and lessons learned, which is especially effective for transferring tacit knowledge that’s hard to document.
Real-world examples can bridge the gap between theory and practice. Case studies highlight how knowledge has been successfully or unsuccessfully applied, offering valuable insights and lessons for others to learn from.
Actionable tips:
Check out the key differences between formal vs informal knowledge transfer to gain valuable insights to enhance your organization’s knowledge management strategy.
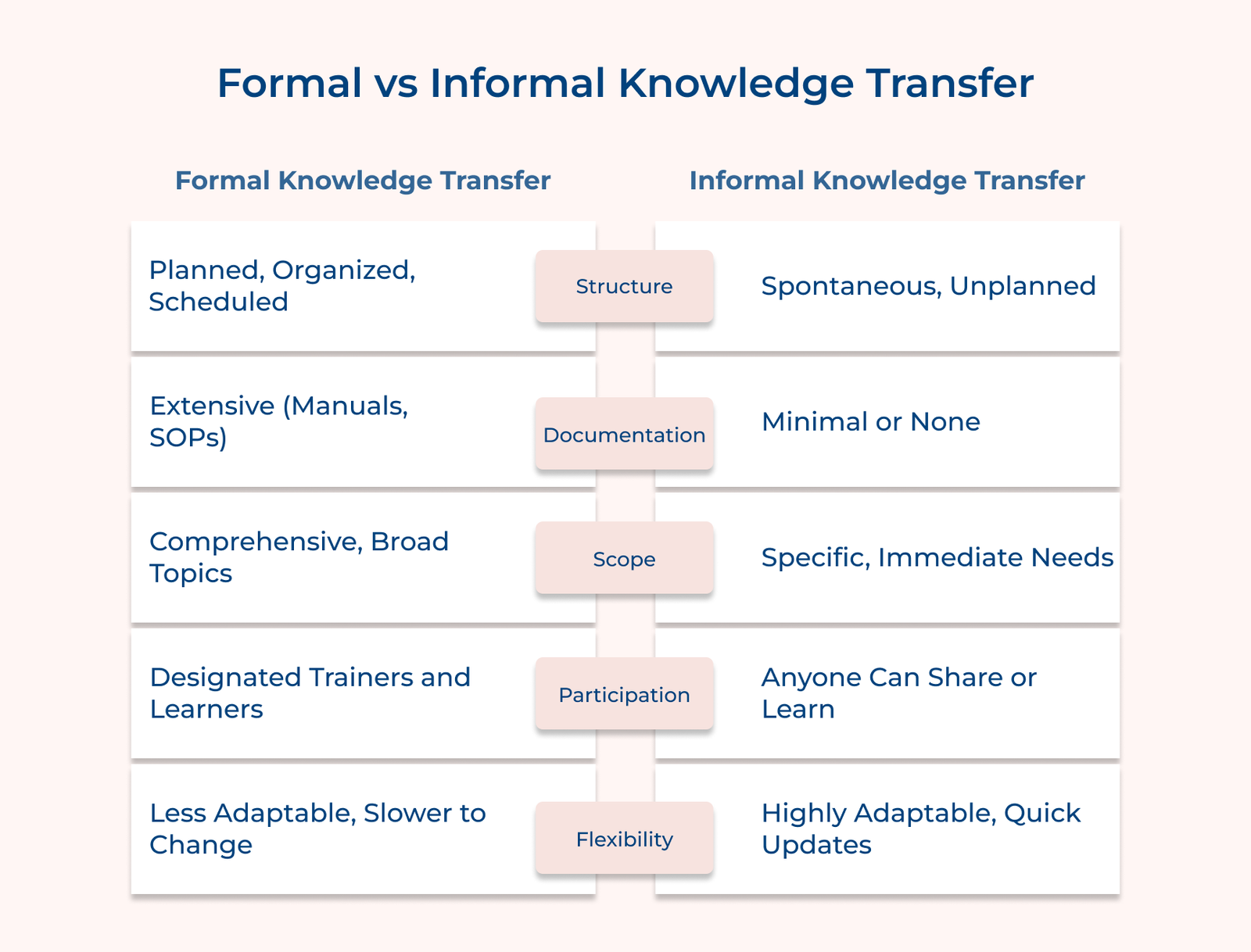
1. Structure and Planning
Knowledge transfer can be structured through scheduled sessions, organized training programs and documented processes. Organizations typically have a clear curriculum outlining what knowledge needs to be transferred and how. Let’s assume that a company might host a series of workshops to train employees on a new software system, complete with specific learning objectives and timelines.
Knowledge transfer can also occur spontaneously through casual interactions, conversations or observations. A senior employee, for instance, might share a valuable tip with a newer colleague during a coffee break or team members might exchange ideas while collaborating on a project.
2. Documentation and Record-keeping
Structured knowledge transfer places a strong emphasis on documentation, creating training materials, manuals and standard operating procedures that serve as consistent reference points. Formal assessments are often included to evaluate the effectiveness of the transfer.
Informal knowledge transfer relies on verbal sharing or demonstrations, with little to no documentation. While the approach allows for immediate and context-specific exchanges, it often results in a lack of permanent records of the knowledge shared.
3. Scope and Depth
Structured knowledge transfer typically covers broader topics and provides comprehensive information, including theoretical foundations or practical applications. A formal training program might thoroughly explore a company’s customer service policy, detailing its philosophy, procedures and scenario handling.
Informal knowledge transfer focuses on specific, immediate needs and practical tips. The approach often shares “tricks of the trade” or contextual knowledge that may not be documented. Let’s consider that an experienced salesperson might share their technique for closing deals with a newcomer.
4. Participation and Engagement
Organized knowledge transfer involves designated trainers or experts with a defined audience of learners. Participation is often mandatory, creating a clear distinction between knowledge providers, with specific time set aside for questions, practice and discussion.
Informal knowledge transfer is collaborative, allowing anyone to be both a provider and recipient depending on the context. Engagement is voluntary, driven by immediate needs or interests, enhancing dynamic, two-way exchanges of information.
5. Flexibility and Adaptability
While comprehensive, structured knowledge transfer can lack flexibility, updating formal training materials or altering established programs is often time-consuming and resource-intensive. It can create delays in incorporating new knowledge into training.
Informal knowledge transfer is highly adaptable, allowing for quick incorporation of new information and responsiveness to changing needs. It enables real-time updates and accommodates unique situations. The flexibility can lead to varying quality and consistency in the knowledge shared, depending on the individuals involved.
Dive into the exploration of knowledge transfer use cases and discover how harnessing the practice can lead to unprecedented growth.
Knowledge transfer is essential for quickly onboarding new hires. Companies can accelerate productivity by sharing organizational knowledge, best practices and cultural norms. The process ensures that valuable institutional knowledge is seamlessly passed on to the next generation of workers.
As experienced employees retire or leave, businesses face the risk of losing valuable expertise. Effective knowledge transfer safeguards critical skills during leadership transitions, nurturing future leaders by passing down strategic insights, industry knowledge and company-specific information.
During mergers or acquisitions, knowledge transfer is vital for blending corporate cultures and operational practices. It aligns processes, shares best practices and facilitates a smooth transition, playing a crucial role in achieving the synergies that justify the corporate moves.
A knowledge transfer plan across departments sparks innovation and enhances problem-solving. Companies can share expertise by breaking down silos, leading to creative solutions and more efficient processes.
As businesses expand into new markets, effective knowledge transfer is crucial for replicating successful practices while adapting to local conditions. It facilitates training for local staff, helps navigate market nuances and ensures consistent quality across all locations.
Ongoing knowledge transfer facilitates a culture of continuous learning and improvement. Businesses remain agile by regularly sharing insights, adapting to changing market conditions and evolving customer needs.
Let’s explore how technology plays a pivotal role in transforming knowledge-sharing management into a strategic advantage.
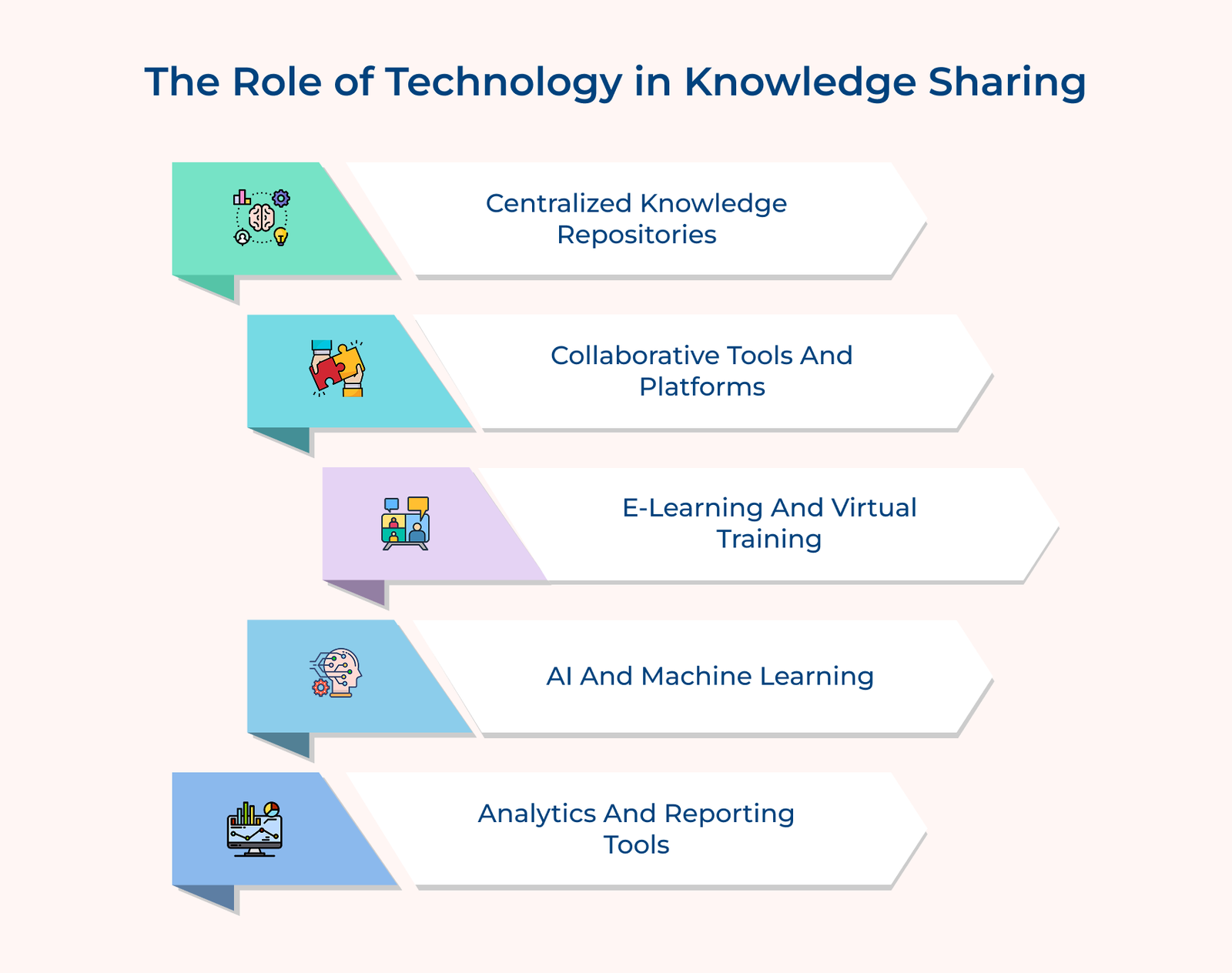
Digital platforms like wikis, intranets and cloud-based document management systems act as centralized hubs for accessing information. They enable easy organization, searching and retrieval of valuable insights, ensuring that all employees have access to the latest updates. The version control allows everyone to stay informed with the most current information.
Technologies like project management software, instant messaging apps and virtual workspaces empower knowledge sharing. The tools enable seamless teamwork by breaking down geographical barriers, allowing employees to ask questions, share ideas and collectively solve problems from anywhere.
Learning management systems (LMS) and virtual reality (VR) are transforming skill development. E-learning platforms offer flexible, self-paced opportunities, while VR delivers immersive, hands-on experiences. Together, the technologies ensure consistent, high-quality training for a large workforce efficiently.
Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning can analyze vast datasets to uncover patterns, extract insights or anticipate future knowledge needs. The technologies personalize learning experiences, recommend relevant content and help identify knowledge gaps within the organization.
Advanced analytics tools offer valuable insights into knowledge sharing and usage within the organization. They track engagement with learning materials, measure the effectiveness of knowledge transfer initiatives and pinpoint areas for improvement. The data-driven approach enables organizations to continually refine their knowledge management strategies for optimal results.
We’ll explore the key barriers to effective knowledge transfer in organizations and share strategies to overcome them, empowering your company to fully leverage its greatest asset—its knowledge.
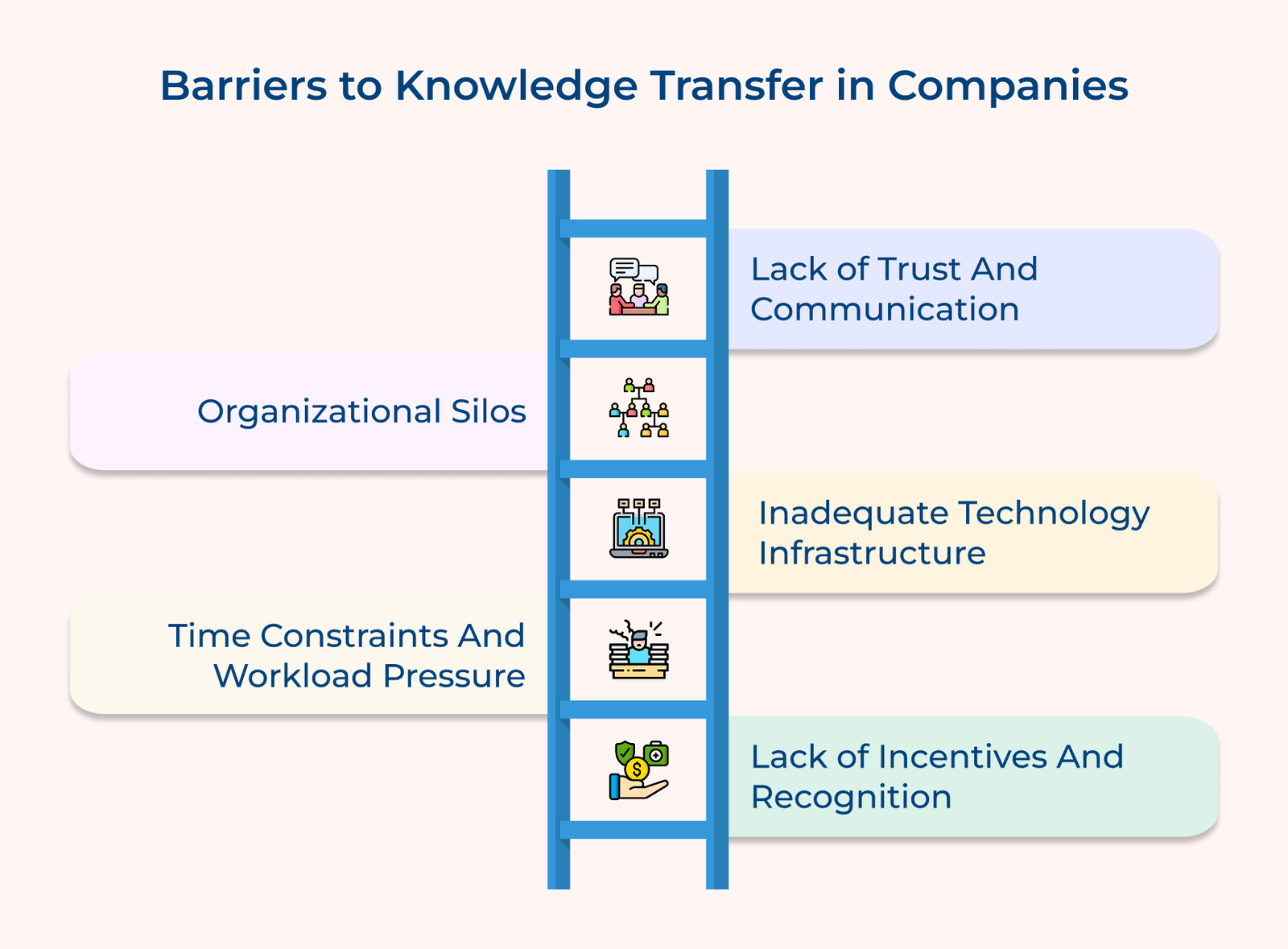
1. Lack of Trust and Communication
When trust is lacking among employees or between staff and management, knowledge sharing suffers. Limited communication channels can further hinder collaboration.
Organize regular team-building activities, establish both formal and informal communication pathways. Encourage leaders to model knowledge-sharing behaviors and reward collaborative efforts to enhance a more connected environment.
2. Organizational Silos
When departments operate in isolation, valuable knowledge gets trapped in silos, stifling cross-functional learning and innovation.
Encourage collaboration through cross-departmental projects and rotational programs. Form interdisciplinary teams for key initiatives and create shared digital spaces where employees can easily collaborate insights.
3. Inadequate Technology Infrastructure
Outdated or poorly integrated knowledge management systems hinder efficient access, sharing and updating of information, leading to duplicated efforts.
Invest in user-friendly, integrated platforms that are accessible on all devices. Provide comprehensive training and regularly update these systems to keep them relevant.
4. Time Constraints and Workload Pressure
When employees feel swamped with daily tasks, knowledge sharing often takes a backseat, resulting in a stagnant knowledge base and missed improvement opportunities.
Allocate dedicated time for knowledge transfer activities. Integrate learning into performance metrics or job descriptions and introduce regular “learning lunches” or knowledge-sharing sessions as part of the work routine.
When employees don’t perceive personal or professional benefits from sharing their knowledge, reluctance can lead to knowledge hoarding and a competitive atmosphere.
Create a recognition and reward system for knowledge sharing. Consider monetary incentives, career advancement opportunities and public acknowledgment. Integrate knowledge transfer into performance evaluations, making it a key factor in promotion decisions.
Knowledge transfer is essential for organizations, blending learning and collaboration to harness collective wisdom. It safeguards valuable insights, drives innovation and ensures operational continuity. Companies can swiftly adapt to market changes and maintain a competitive edge by facilitating information flow at all levels.
Effective transfer of knowledge boosts operational efficiency and client engagement. Businesses streamline processes, reduce errors and enhance productivity by sharing best practices. Well-informed employees can deliver personalized customer service, resulting in higher client satisfaction and loyalty.
A Knowledge Transfer (KT) session is a structured meeting designed to share valuable information, skills and best practices between individuals or teams. The sessions facilitate effective communication of key insights, making them essential for onboarding new employees, boosting collaboration and enhancing productivity.
Knowledge transfer is vital for effective problem-solving in business, allowing team members to share insights and expertise. Organizations can innovate, make better decisions and avoid repeating mistakes by harnessing collective knowledge. The collaborative approach cultivates a culture of learning, enabling businesses to respond swiftly to challenges and boost productivity in a competitive landscape.
The goal of knowledge transfer is to share information, skills and expertise within an organization. The process boosts collaboration, drives innovation and preserves critical knowledge from experienced employees. Effective transfer empowers teams, enhances performance and enhances a learning culture, enabling organizations to thrive.
Common methods for knowledge transfer include mentoring programs, job shadowing, training sessions and process documentation. Collaborative platforms, cross-functional teams and communities of practice also play key roles. Technology-driven approaches like e-learning modules, webinars and internal wikis enhance knowledge sharing across the organization.
Measuring knowledge transfer effectiveness involves tracking metrics like knowledge access frequency, contributions to knowledge bases and process efficiency improvements. Additional indicators include reduced training time, higher innovation rates and enhanced problem-solving abilities. Employee surveys and assessments can help measure how employees value knowledge transfer efforts.
Market better, sell faster and support smarter with Veemo’s Conversation Customer Engagement suite of products.
Unify all your customer data in one platform to deliver contextual responses. Get a 360 degree view of the customer lifecycle without switching tools.
Connect with the tools you love to reduce manual activities and sync your business workflows for a seamless experience.
 https://veemo.io/wp-content/uploads/2025/12/customer-connection.png
1256
2400
Indrasish Singha
https://veemo.io/wp-content/uploads/2024/11/veemo.svg
Indrasish Singha2026-02-06 09:11:372026-01-19 09:14:05What is Customer Connection: Mistakes, Metrics & Examples
https://veemo.io/wp-content/uploads/2025/12/customer-connection.png
1256
2400
Indrasish Singha
https://veemo.io/wp-content/uploads/2024/11/veemo.svg
Indrasish Singha2026-02-06 09:11:372026-01-19 09:14:05What is Customer Connection: Mistakes, Metrics & Examples https://veemo.io/wp-content/uploads/2025/12/complaint-management.png
1256
2400
Indrasish Singha
https://veemo.io/wp-content/uploads/2024/11/veemo.svg
Indrasish Singha2026-02-03 09:04:022026-01-19 09:10:02What is Complaint Management? Importance, Key Steps & Strategies
https://veemo.io/wp-content/uploads/2025/12/complaint-management.png
1256
2400
Indrasish Singha
https://veemo.io/wp-content/uploads/2024/11/veemo.svg
Indrasish Singha2026-02-03 09:04:022026-01-19 09:10:02What is Complaint Management? Importance, Key Steps & Strategies https://veemo.io/wp-content/uploads/2025/12/AI-Self-Service.png
1256
2400
Indrasish Singha
https://veemo.io/wp-content/uploads/2024/11/veemo.svg
Indrasish Singha2026-01-26 09:52:482026-01-13 10:17:07What is AI Self Service? Benefits, Key Metrics and Best Practices
https://veemo.io/wp-content/uploads/2025/12/AI-Self-Service.png
1256
2400
Indrasish Singha
https://veemo.io/wp-content/uploads/2024/11/veemo.svg
Indrasish Singha2026-01-26 09:52:482026-01-13 10:17:07What is AI Self Service? Benefits, Key Metrics and Best PracticesGrow Customer Relationships and stronger team collaboration with our range of products across the Conversational Engagement Suite.
 How to Create a Customer-Centric Company: 8 Strategies
Scroll to top
How to Create a Customer-Centric Company: 8 Strategies
Scroll to top